Feasibility of confocal endomicroscopy in the diagnosis of pediatric gastrointestinal disorders
- PMID: 19437560
- PMCID: PMC2682235
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.15.2214
Feasibility of confocal endomicroscopy in the diagnosis of pediatric gastrointestinal disorders
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the feasibility and utility of confocal laser endomicroscopy (CLE) in the description of normal gastrointestinal (GI) mucosa and in the diagnosis of GI disorders in children, in comparison to histology.
Methods: Forty-four patients (19 female) median age 10.9 years (range 0.7-16.6 years) with suspected or known GI pathology underwent esophago-gastro-duodenoscopy (OGD) (n = 36) and/or ileocolonoscopy (IC) (n = 31) with CLE using sodium fluorescein and acriflavine as contrast agents. Histological sections were compared with same site confocal images by two experienced pediatric and GI histopathologists and endoscopists, respectively.
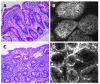
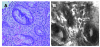
Results: Duodenum and ileum were intubated in all but one patient undergoing OGD and IC. The median procedure time was 16.4 min (range 7-25 min) for OGD and 27.9 min (range 15-45 min) for IC. A total of 4798 confocal images were compared with 153 biopsies from the upper GI tract from 36 procedures, and 4661 confocal images were compared with 188 biopsies from the ileocolon from 31 procedures. Confocal images were comparable to conventional histology both in normal and in pathological conditions such as esophagitis, Helicobacter pylori gastritis, celiac disease, inflammatory bowel disease, colonic heterotopia, and graft versus host disease.
Conclusion: CLE offers the prospect of targeting biopsies to abnormal mucosa, thereby increasing diagnostic yield, reducing the number of biopsies, decreasing the burden on the histopathological services, and reducing costs.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Confocal laser endomicroscopy in the "in vivo" histological diagnosis of the gastrointestinal tract.World J Gastroenterol. 2009 Dec 14;15(46):5770-5. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.5770. World J Gastroenterol. 2009. PMID: 19998496 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison between two types of confocal laser endomicroscopy in gastrointestinal tract.J Dig Dis. 2015 May;16(5):279-85. doi: 10.1111/1751-2980.12245. J Dig Dis. 2015. PMID: 25762057 Clinical Trial.
-
Confocal laser endomicroscopy in gastrointestinal diseases.J Biophotonics. 2011 Aug;4(7-8):498-508. doi: 10.1002/jbio.201100022. Epub 2011 May 13. J Biophotonics. 2011. PMID: 21567975 Review.
-
A study on confocal endomicroscopy in comparison with histopathology for polypoidal lesions of the gastrointestinal tract: A prospective single-centre experience.Indian J Gastroenterol. 2019 Aug;38(4):332-337. doi: 10.1007/s12664-019-00973-4. Epub 2019 Aug 24. Indian J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31446613
-
[Microscopy of the gastrointestinal tract: confocal endomicroscopy - clinical and scientific benefits].Zentralbl Chir. 2014 Aug;139(4):428-33. doi: 10.1055/s-0032-1327970. Epub 2013 Jul 3. Zentralbl Chir. 2014. PMID: 23824617 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Ultra high magnification endoscopy: Is seeing really believing?World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2012 Oct 16;4(10):462-71. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v4.i10.462. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2012. PMID: 23189217 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative Diagnosis of Atrophic Gastritis by Probe-Based Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Mar 2;2020:9847591. doi: 10.1155/2020/9847591. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32190694 Free PMC article.
-
Position paper: The potential role of optical biopsy in the study and diagnosis of environmental enteric dysfunction.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017 Dec;14(12):727-738. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2017.147. Epub 2017 Nov 15. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017. PMID: 29139480 Review.
-
Diagnosis of gastric intraepithelial neoplasia by narrow-band imaging and confocal laser endomicroscopy.World J Gastroenterol. 2012 Sep 14;18(34):4771-80. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i34.4771. World J Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 23002348 Free PMC article.
-
Confocal laser endomicroscopy in the "in vivo" histological diagnosis of the gastrointestinal tract.World J Gastroenterol. 2009 Dec 14;15(46):5770-5. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.5770. World J Gastroenterol. 2009. PMID: 19998496 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bosco JJ, Barkun AN, Isenberg GA, Nguyen CC, Petersen BT, Silverman WB, Slivka A, Taitelbaum G, Ginsberg GG. Gastrointestinal endoscopes: May 2003. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003;58:822–830. - PubMed
-
- Kiesslich R, Fritsch J, Holtmann M, Koehler HH, Stolte M, Kanzler S, Nafe B, Jung M, Galle PR, Neurath MF. Methylene blue-aided chromoendoscopy for the detection of intraepithelial neoplasia and colon cancer in ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology. 2003;124:880–888. - PubMed
-
- Gono K, Obi T, Yamaguchi M, Ohyama N, Machida H, Sano Y, Yoshida S, Hamamoto Y, Endo T. Appearance of enhanced tissue features in narrow-band endoscopic imaging. J Biomed Opt. 2004;9:568–577. - PubMed
-
- Jung M, Kiesslich R. Chromoendoscopy and intravital staining techniques. Baillieres Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 1999;13:11–19. - PubMed
-
- Delaney PM, Harris MR. Fiberoptics in confocal microscopy. In: Pawley JB, editor. Handbook of biological confocal microscopy. New York: Springer; 2006. pp. 501–515.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

