Targeting and regulation of reactive oxygen species generation by Nox family NADPH oxidases
- PMID: 19438290
- PMCID: PMC2782575
- DOI: 10.1089/ars.2009.2637
Targeting and regulation of reactive oxygen species generation by Nox family NADPH oxidases
Abstract
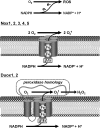
Nox family NADPH oxidases serve a variety of functions requiring reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation, including antimicrobial defense, biosynthetic processes, oxygen sensing, and redox-based cellular signaling. We explored targeting, assembly, and activation of several Nox family oxidases, since ROS production appears to be regulated both spatially and temporally. Nox1 and Nox3 are similar to the phagocytic (Nox2-based) oxidase, functioning as multicomponent superoxide-generating enzymes. Factors regulating their activities include cytosolic activator and organizer proteins and GTP-Rac. Their regulation varies, with the following rank order: Nox2 > Nox1 > Nox3. Determinants of subcellular targeting include: (a) formation of Nox-p22(phox) heterodimeric complexes allowing plasma membrane translocation, (b) phospholipids-binding specificities of PX domain-containing organizer proteins (p47(phox) or Nox organizer 1 (Noxo1 and p40(phox)), and (c) variably splicing of Noxo1 PX domains directing them to nuclear or plasma membranes. Dual oxidases (Duox1 and Duox2) are targeted by different mechanisms. Plasma membrane targeting results in H(2)O(2) release, not superoxide, to support extracellular peroxidases. Human Duox1 and Duox2 have no demonstrable peroxidase activity, despite their extensive homology with heme peroxidases. The dual oxidases were reconstituted by Duox activator 2 (Duoxa2) or two Duoxa1 variants, which dictate maturation, subcellular localization, and the type of ROS generated by forming stable complexes with Duox.
Figures






References
-
- Abo A. Pick E. Hall A. Totty N. Teahan CG. Segal AW. Activation of the NADPH oxidase involves the small GTP-binding protein p21rac1. Nature. 1991;353:668–670. - PubMed
-
- Ago T. Nunoi H. Ito T. Sumimoto H. Mechanism for phosphorylation-induced activation of the phagocyte NADPH oxidase protein p47phox. Triple replacement of serines 303, 304, and 328 with aspartates disrupts the SH3 domain-mediated intramolecular interaction in p47(phox), thereby activating the oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:33644–33653. - PubMed
-
- Ambasta RK. Kumar P. Griendling KK. Schmidt HHHW. Busse R. Brandes RP. Direct interaction of the novel Nox proteins with p22phox is required for the formation of a functionally active NADPH oxidase. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:45935–45941. - PubMed
-
- Ameziane–El-Hassani R. Morand S. Boucher JL. Frapart YM. Apostolou D. Agnandji D. Gnidehou S. Ohayon R. Noel–Hudson MS. Francon J. Lalaoui K. Virion A. Dupuy C. Dual oxidase-2 has an intrinsic Ca2+-dependent H2O2-generating activity. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:30046–30054. - PubMed
-
- Anderson KE. Boyle K. Davidson K. Chessa TA. Kulkarni S. Jarvis GE. Sindrilaru A. Scharffetter–Kochanek K. Rausch O. Stephens LR. Hawkins PT. CD18-dependent activation of the neutrophil NADPH oxidase during phagocytosis of E. coli or S. aureus is regulated by Class III but not Class I or II PI3Ks. Blood. 2008;112:5205–5211. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

