Source gene composition and gene conversion of the AluYh and AluYi lineages of retrotransposons
- PMID: 19442302
- PMCID: PMC2686708
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2148-9-102
Source gene composition and gene conversion of the AluYh and AluYi lineages of retrotransposons
Abstract
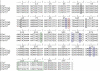
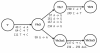
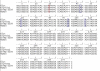
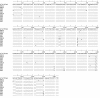
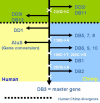
Background: Alu elements are a family of SINE retrotransposons in primates. They are classified into subfamilies according to specific diagnostic mutations from the general Alu consensus. It is now believed that there may be several retrotranspositionally-competent source genes within an Alu subfamily. In this study, subfamilies falling on the AluYi and AluYh lineages, and the AluYg6 subfamily, are assessed for the presence of secondary source genes, and the influence of gene conversion on the AluYh and AluYi lineages is also described.
Results: The AluYh7 and AluYi6 subfamilies appear to contain multiple source genes. The novel subfamilies AluYh3a1 and AluYh3a3 are described, for which there is no convincing evidence to suggest the presence of secondary sources. The mutational substructure of AluYh3a3 can be explained completely by inference of single master gene. A complete backwards gene conversion event appears to have inactivated the AluYh3a3 master gene in humans. Polymorphism data suggest a larger number of secondary source elements may be active in the AluYg6 family than previously thought.
Conclusion: It is clear that there is considerable variation in the number of source genes present in each of the young Alu subfamilies. This can range from a single master source gene, as for AluYh3a3, to as many as 14 source elements in AluYi6.
Figures


References
-
- Lander ES, Linton LM, Birren B, Nusbaum C, Zody MC, Baldwin J, Devon K, Dewar K, Doyle M, FitzHugh W, Funke R, Gage D, Harris K, Heaford A, Howland J, Kann L, Lehoczky J, LeVine R, McEwan P, McKernan K, Meldrim J, Mesirov JP, Miranda C, Morris W, Naylor J, Raymond C, Rosetti M, Santos R, Sheridan A, Sougnez C, Stange-Thomann N, Stojanovic N, Subramanian A, Wyman D, Rogers J, Sulston J, Ainscough R, Beck S, Bentley D, Burton J, Clee C, Carter N, Coulson A, Deadman R, Deloukas P, Dunham A, Dunham I, Durbin R, French L, Grafham D, Gregory S, Hubbard T, Humphray S, Hunt A, Jones M, Lloyd C, McMurray A, Matthews L, Mercer S, Milne S, Mullikin JC, Mungall A, Plumb R, Ross M, Shownkeen R, Sims S, Waterston RH, Wilson RK, Hillier LW, McPherson JD, Marra MA, Mardis ER, Fulton LA, Chinwalla AT, Pepin KH, Gish WR, Chissoe SL, Wendl MC, Delehaunty KD, Miner TL, Delehaunty A, Kramer JB, Cook LL, Fulton RS, Johnson DL, Minx PJ, Clifton SW, Hawkins T, Branscomb E, Predki P, Richardson P, Wenning S, Slezak T, Doggett N, Cheng JF, Olsen A, Lucas S, Elkin C, Uberbacher E, Frazier M, Gibbs RA, Muzny DM, Scherer SE, Bouck JB, Sodergren EJ, Worley KC, Rives CM, Gorrell JH, Metzker ML, Naylor SL, Kucherlapati RS, Nelson DL, Weinstock GM, Sakaki Y, Fujiyama A, Hattori M, Yada T, Toyoda A, Itoh T, Kawagoe C, Watanabe H, Totoki Y, Taylor T, Weissenbach J, Heilig R, Saurin W, Artiguenave F, Brottier P, Bruls T, Pelletier E, Robert C, Wincker P, Rosenthal A, Platzer M, Nyakatura G, Taudien S, Rump A, Yang HM, Yu J, Wang J, Huang GY, Gu J, Hood L, Rowen L, Madan A, Qin SZ, Davis RW, Federspiel NA, Abola AP, Proctor MJ, Myers RM, Schmutz J, Dickson M, Grimwood J, Cox DR, Olson MV, Kaul R, Raymond C, Shimizu N, Kawasaki K, Minoshima S, Evans GA, Athanasiou M, Schultz R, Roe BA, Chen F, Pan HQ, Ramser J, Lehrach H, Reinhardt R, McCombie WR, de la Bastide M, Dedhia N, Blocker H, Hornischer K, Nordsiek G, Agarwala R, Aravind L, Bailey JA, Bateman A, Batzoglou S, Birney E, Bork P, Brown DG, Burge CB, Cerutti L, Chen HC, Church D, Clamp M, Copley RR, Doerks T, Eddy SR, Eichler EE, Furey TS, Galagan J, Gilbert JGR, Harmon C, Hayashizaki Y, Haussler D, Hermjakob H, Hokamp K, Jang WH, Johnson LS, Jones TA, Kasif S, Kaspryzk A, Kennedy S, Kent WJ, Kitts P, Koonin EV, Korf I, Kulp D, Lancet D, Lowe TM, McLysaght A, Mikkelsen T, Moran JV, Mulder N, Pollara VJ, Ponting CP, Schuler G, Schultz JR, Slater G, Smit AFA, Stupka E, Szustakowki J, Thierry-Mieg D, Thierry-Mieg J, Wagner L, Wallis J, Wheeler R, Williams A, Wolf YI, Wolfe KH, Yang SP, Yeh RF, Collins F, Guyer MS, Peterson J, Felsenfeld A, Wetterstrand KA, Patrinos A, Morgan MJ. Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature. 2001;409:860–921. doi: 10.1038/35057062. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Deininger PL, Batzer MA, Hutchison CA, Edgell MH. Master genes in mammalian repetitive DNA amplification. Trends in Genetics. 1992;8:307–311. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

