Systematic identification of transcription factors associated with patient survival in cancers
- PMID: 19442316
- PMCID: PMC2686740
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-225
Systematic identification of transcription factors associated with patient survival in cancers
Abstract
Background: Aberrant activation or expression of transcription factors has been implicated in the tumorigenesis of various types of cancer. In spite of the prevalent application of microarray experiments for profiling gene expression in cancer samples, they provide limited information regarding the activities of transcription factors. However, the association between transcription factors and cancers is largely dependent on the transcription regulatory activities rather than mRNA expression levels.
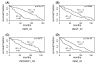
Results: In this paper, we propose a computational approach that integrates microarray expression data with the transcription factor binding site information to systematically identify transcription factors associated with patient survival given a specific cancer type. This approach was applied to two gene expression data sets for breast cancer and acute myeloid leukemia. We found that two transcription factor families, the steroid nuclear receptor family and the ATF/CREB family, are significantly correlated with the survival of patients with breast cancer; and that a transcription factor named T-cell acute lymphocytic leukemia 1 is significantly correlated with acute myeloid leukemia patient survival.
Conclusion: Our analysis identifies transcription factors associating with patient survival and provides insight into the regulatory mechanism underlying the breast cancer and leukemia. The transcription factors identified by our method are biologically meaningful and consistent with prior knowledge. As an insightful tool, this approach can also be applied to other microarray cancer data sets to help researchers better understand the intricate relationship between transcription factors and diseases.
Figures
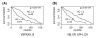



Similar articles
-
Gene expression profiling combined with bioinformatics analysis identify biomarkers for Parkinson disease.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e52319. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052319. Epub 2012 Dec 28. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23284986 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-class cancer classification via partial least squares with gene expression profiles.Bioinformatics. 2002 Sep;18(9):1216-26. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/18.9.1216. Bioinformatics. 2002. PMID: 12217913
-
Transcriptional regulatory networks downstream of TAL1/SCL in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Blood. 2006 Aug 1;108(3):986-92. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-08-3482. Epub 2006 Apr 18. Blood. 2006. PMID: 16621969 Free PMC article.
-
Combined gene expression and DNA occupancy profiling as a strategy to identify therapeutic target(s) in t(8;21) acute myeloid leukemia.Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2013;23(2):103-13. doi: 10.1615/critreveukaryotgeneexpr.2013006917. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2013. PMID: 23582033 Review.
-
Transcription factors of the bHLH and LIM families: synergistic mediators of T cell acute leukemia?Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1997;220:55-65. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-60479-9_4. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1997. PMID: 9103675 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Identification of Transcription Factor/Gene Axis in Colon Cancer Using a Methylome Approach.Front Genet. 2020 Jul 31;11:864. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00864. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 32849837 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a Transcription Factor Signature That Can Predict Breast Cancer Survival.Comput Math Methods Med. 2021 Feb 19;2021:2649123. doi: 10.1155/2021/2649123. eCollection 2021. Comput Math Methods Med. 2021. PMID: 33688372 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome-wide signatures of tumor stage in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma: connecting copy number variation, methylation and transcription factor activity.Genome Med. 2014 Dec 11;6(12):117. doi: 10.1186/s13073-014-0117-z. eCollection 2014. Genome Med. 2014. PMID: 25648588 Free PMC article.
-
REACTIN: regulatory activity inference of transcription factors underlying human diseases with application to breast cancer.BMC Genomics. 2013 Jul 26;14:504. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-504. BMC Genomics. 2013. PMID: 23885756 Free PMC article.
-
DPRP: a database of phenotype-specific regulatory programs derived from transcription factor binding data.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Jan;42(Database issue):D178-83. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1254. Epub 2013 Dec 2. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24302579 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Muller H, Helin K. The E2F transcription factors: key regulators of cell proliferation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000;1470:M1–12. - PubMed
-
- Sakakura C, Hagiwara A, Miyagawa K, Nakashima S, Yoshikawa T, Kin S, Nakase Y, Ito K, Yamagishi H, Yazumi S, et al. Frequent downregulation of the runt domain transcription factors RUNX1, RUNX3 and their cofactor CBFB in gastric cancer. Int J Cancer. 2005;113:221–228. doi: 10.1002/ijc.20551. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

