Renal biopsy in the very elderly
- PMID: 19443626
- PMCID: PMC2689880
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.00990209
Renal biopsy in the very elderly
Abstract
Background and objectives: Data regarding renal biopsy in the very elderly (>or=age 80 yr) are extremely limited. The aim of this study was to examine the causes of renal disease and their clinical presentations in very elderly patients who underwent native renal biopsy.
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: All native renal biopsies (n = 235 including 106 men, 129 women) performed in patients aged >or=80 yr over a 3.67-yr period were retrospectively identified. Results were compared with a control group of 264 patients aged 60 to 61 who were biopsied over the same period.
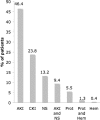
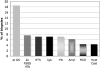
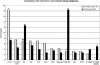
Results: The indications for biopsy were acute kidney injury (AKI) in 46.4%, chronic-progressive kidney injury in 23.8%, nephrotic syndrome (NS) in 13.2%, NS with AKI in 9.4%, and isolated proteinuria in 5.5%. Pauci-immune GN was the most frequent diagnosis (19%), followed by focal segmental glomerulosclerosis secondary to hypertension (7.6%), hypertensive nephrosclerosis (7.1%), IgA nephropathy (7.1%) and membranous nephropathy (7.1%). Comparison with the control group showed pauci-immune GN to be more frequent (P < 0.001) and diabetic glomerulosclerosis (P < 0.001) and membranous nephropathy (P < 0.05) less frequent in the very elderly. Diagnostic information had the potential to modify treatment in 67% of biopsies from the very elderly, particularly in those with AKI or NS.
Conclusions: Renal biopsy in very elderly patients is a valuable diagnostic tool that should be offered in clinical settings with maximal potential benefit. Advanced age per se should no longer be considered a contraindication to renal biopsy.
Figures
References
-
- Wan H, Sengupta M, Velkoff V, DeBarros K: 65+ in the United States: 2005. In: Current Population Reports U.S. Census Bureau. Washington DC: U.S. Government Printing Office, 2005, pp 23–209
-
- Abrass CK: Renal biopsy in the elderly. Am J Kidney Dis 35: 544–546, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Nair R, Bell JM, Walker PD: Renal biopsy in patients aged 80 years and older. Am J Kidney Dis 44: 618–626, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Haas M, Spargo BH, Wit EJ, Meehan SM: Etiologies and outcome of acute renal insufficiency in older adults: A renal biopsy study of 259 cases. Am J Kidney Dis 35: 433–447, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Ferro G, Dattolo P, Nigrelli S, Michelassi S, Pizzarelli F: Clinical pathological correlates of renal biopsy in elderly patients. Clin Nephrol 65: 243–247, 2006 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

