Albuminuria and kidney function independently predict cardiovascular and renal outcomes in diabetes
- PMID: 19443635
- PMCID: PMC2723977
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2008121270
Albuminuria and kidney function independently predict cardiovascular and renal outcomes in diabetes
Abstract
There are limited data regarding whether albuminuria and reduced estimated GFR (eGFR) are separate and independent risk factors for cardiovascular and renal events among individuals with type 2 diabetes. The Action in Diabetes and Vascular disease: preterAx and diamicroN-MR Controlled Evaluation (ADVANCE) study examined the effects of routine BP lowering on adverse outcomes in type 2 diabetes. We investigated the effects of urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR) and eGFR on the risk for cardiovascular and renal events in 10,640 patients with available data. During an average 4.3-yr follow-up, 938 (8.8%) patients experienced a cardiovascular event and 107 (1.0%) experienced a renal event. The multivariable-adjusted hazard ratio for cardiovascular events was 2.48 (95% confidence interval 1.74 to 3.52) for every 10-fold increase in baseline UACR and 2.20 (95% confidence interval 1.09 to 4.43) for every halving of baseline eGFR, after adjustment for regression dilution. There was no evidence of interaction between the effects of higher UACR and lower eGFR. Patients with both UACR >300 mg/g and eGFR <60 ml/min per 1.73 m(2) at baseline had a 3.2-fold higher risk for cardiovascular events and a 22.2-fold higher risk for renal events, compared with patients with neither of these risk factors. In conclusion, high albuminuria and low eGFR are independent risk factors for cardiovascular and renal events among patients with type 2 diabetes.
Figures
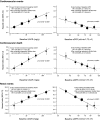
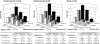


References
-
- International Diabetes Federation: Diabetes Atlas 2006, 3rd Ed., Brussels, International Diabetes Federation, 2006
-
- Asia Pacific Cohort Studies Collaboration: The effects of diabetes on the risks of major cardiovascular diseases and death in the Asia-Pacific region. The Asia Pacific Cohort Studies Collaboration. Diabetes Care 26: 360–366, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Gerstein HC, Mann JF, Yi Q, Zinman B, Dinneen SF, Hoogwerf B, Hallé JP, Young J, Rashkow A, Joyce C, Nawaz S, Yusuf SHOPE Study Investigators: Albuminuria and risk of cardiovascular events, death, and heart failure in diabetic and nondiabetic individuals. JAMA 286: 421–426, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Valmadrid CT, Klein R, Moss SE, Klein BE: The risk of cardiovascular disease mortality associated with microalbuminuria and gross proteinuria in persons with older-onset diabetes mellitus. Arch Intern Med 160: 1093–1100, 2000 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

