A reduction in Pten tumor suppressor activity promotes ErbB-2-induced mouse prostate adenocarcinoma formation through the activation of signaling cascades downstream of PDK1
- PMID: 19443706
- PMCID: PMC2684171
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2009.080859
A reduction in Pten tumor suppressor activity promotes ErbB-2-induced mouse prostate adenocarcinoma formation through the activation of signaling cascades downstream of PDK1
Abstract
Loss of function at the Pten tumor-suppressor locus is a common genetic modification found in human prostate cancer. While recent in vivo and in vitro data support an important role of aberrant ErbB-2 signaling to clinically relevant prostate target genes, such as cyclin D1, the role of Pten in ErbB-2-induced prostate epithelial proliferation is not well understood. In the Pten-deficient prostate cancer cell line, LNCaP, restoration of Pten was able to inhibit ErbB-2- and heregulin-induced cell cycle progression, as well as cyclin D1 protein levels and promoter activity. Previously, we established that probasin-driven ErbB-2 transgenic mice presented with high-grade prostate intraepithelial neoplasia and increased nuclear cyclin D1 levels. We show that mono-allelic loss of pten in the probasin-driven-ErbB-2 model resulted in increased nuclear cyclin D1 and proliferating cell nuclear antigen levels and decreased disease latency compared to either individual genetic model and, unlike the probasin-driven-ErbB-2 mice, progression to adenocarcinoma. Activated 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 was observed during cancer initiation combined with the activation of p70S6K (phospho-T389) and inactivation of the 4E-binding protein-1 (phosphorylated on T37/46) and was primarily restricted to those cases of prostate cancer that had progressed to adenocarcinoma. Activation of mTOR was not seen. Our data demonstrates that Pten functions downstream of ErbB-2 to restrict prostate epithelial transformation by blocking full activation of the PDK1 signaling cascade.
Figures

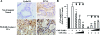

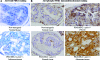
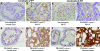
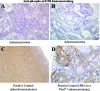


References
-
- Shi Y, Chatterjee SJ, Brands FH, Shi SR, Pootrakul L, Taylor CR, Datar R, Cote RJ. Role of coordinated molecular alterations in the development of androgen-independent prostate cancer: an in vitro model that corroborates clinical observations. BJU Int. 2006;97:170–178. - PubMed
-
- Dai B, Kong YY, Ye DW, Ma CG, Zhou XY, Yao XD. Human epidermal growth factor receptor type 2 protein expression in Chinese metastatic prostate cancer patients correlates with cancer specific survival and increases after exposure to hormonal therapy. Asian J Androl. 2008;10:701–709. - PubMed
-
- Casimiro MC, Rodriguez O, Pootrakul L, Fricke ST, Ostrowski M, Rabbani S, Datar R, Cote RJ, Pestell R, Albanese C. ErbB-2 induces the cyclin D1 gene in prostate epithelial cells in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res. 2007;67:4364–4372.. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

