The StrongWomen-Healthy Hearts program: reducing cardiovascular disease risk factors in rural sedentary, overweight, and obese midlife and older women
- PMID: 19443826
- PMCID: PMC2696662
- DOI: 10.2105/AJPH.2008.145581
The StrongWomen-Healthy Hearts program: reducing cardiovascular disease risk factors in rural sedentary, overweight, and obese midlife and older women
Abstract
Objectives: We tested a community-based intervention designed to reduce cardiovascular disease risk in sedentary midlife and older women who were overweight or obese.
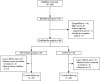
Methods: In a randomized controlled trial conducted in 8 counties in Arkansas and Kansas, counties were assigned to the intervention (a 12-week twice-weekly heart health program) group or to the delayed-intervention control group. Ten to fifteen women were selected from each site, and participants' weight, waist circumference, diet, physical activity, and self-efficacy were measured before and after the intervention. Data were analyzed with multiple regressions.
Results: Compared with the control group, participants in the intervention group had a significant decrease in body weight (-2.1 kg; 95% confidence interval [CI] = -3.2, -1.0), waist circumference (-2.3 in; 95% CI = -4.2, -0.5), and energy intake (-390 kcal/day; 95% CI = -598, -183); an increase in activity (+1637 steps/day; 95% CI = 712, 2562); and an increase in self-efficacy for dietary and physical activity behaviors.
Conclusions: Our results suggest that a community-based program can improve self-efficacy, increase physical activity, and decrease energy intake, resulting in decreased waist circumference and body weight among at-risk women.
Figures
References
-
- Rosamond W, Flegal K, Friday G, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2007 update: a report from the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Committee. Circulation 2007;115:e69–e171 - PubMed
-
- Gerberding G. Healthy Aging: Preventing Disease and Improving Quality of Life Among Older Americans 2006. Atlanta, GA: Coordinating Center for Health Promotion, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 2006
-
- He W, Sengupta M, Velkoff V, DeBarros K. 65+ in the United States: 2005 Washington, DC: US Census Bureau; 2005
-
- Mozaffarian D, Fried L, Burke G, Fitzpatrick A, Siscovick D. Lifestyles of older adults: can we influence cardiovascular risk in older adults? Am J Geriatr Cardiol 2004;13(3):153–160 - PubMed
-
- Guenther PM, Dodd KW, Reedy J, Krebs-Smith SM. Most Americans eat much less than recommended amounts of fruits and vegetables. J Am Diet Assoc 2006;106(9):1371–1379 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources