Effects of poor and short sleep on glucose metabolism and obesity risk
- PMID: 19444258
- PMCID: PMC4457292
- DOI: 10.1038/nrendo.2009.23
Effects of poor and short sleep on glucose metabolism and obesity risk
Abstract
The importance of sleep to hormones and glucose metabolism was first documented more than four decades ago. Since then, sleep curtailment has become an endemic behavior in modern society. In addition, the prevalence of sleep disorders, particularly obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), has increased. OSA is very common in endocrine and metabolic disorders, but often remains undiagnosed. This Review summarizes the laboratory and epidemiologic evidence that suggests how sleep loss, either behavioral or disease-related, and poor quality of sleep might promote the development of obesity and diabetes mellitus, and exacerbate existing endocrine conditions. Treatment of sleep disorders has the potential to improve glucose metabolism and energy balance. Screening for habitual sleep patterns and OSA might be critically important for patients with endocrine and metabolic disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
E. Van Cauter has declared associations with the following companies: Actelyon and Sanofi-Aventis. See the article online for full details of the relationships. R. Leprout, K. Spiegel and E. Tasali declared no competing interests.
Figures
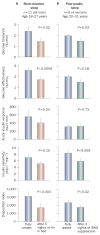
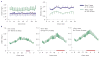
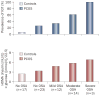
References
-
- Gronfier C, Brandenberger G. Ultradian rhythms in pituitary and adrenal hormones: their relations to sleep. Sleep Med Rev. 1998;2:17–29. - PubMed
-
- Van Cauter E. Endocrine physiology. In: Kryger M, Roth T, Dement WC, editors. Principles and Practice of Sleep Medicine. 4. Elsevier–Saunders; Philadelphia: 2005. pp. 266–282.
-
- Sakurai T. The neural circuit of orexin (hypocretin): maintaining sleep and wakefulness. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2007;8:171–181. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK-0716960/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL075025/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL075079/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL-075025/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL-075079/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000055/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR013642/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG-11412/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK071696/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P60 DK-20595/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P60 DK020595/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG011412/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

