Innate immunity turned inside-out: antimicrobial defense by phagocyte extracellular traps
- PMID: 19444424
- PMCID: PMC2707954
- DOI: 10.1007/s00109-009-0481-0
Innate immunity turned inside-out: antimicrobial defense by phagocyte extracellular traps
Abstract
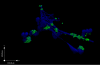
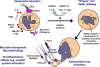
The formation of extracellular traps (ETs) by phagocytic cells has been recognized as a novel and important mechanism of the host innate immune response against infections. ETs are formed by different host immune cells such as neutrophils, mast cells, and eosinophils after stimulation with mitogens, cytokines, or pathogens themselves, in a process dependent upon induction of a reactive-oxygen-species-mediated signaling cascade. ETs consist of nuclear or mitochondrial DNA as a backbone with embedded antimicrobial peptides, histones, and cell-specific proteases and thereby provide a matrix to entrap and kill microbes and to induce the contact system. This review summarizes the latest research on ETs and their role in innate immunity and host innate defense. Attention is also given to mechanisms by which certain leading bacterial pathogens have evolved to avoid entrapment and killing in these specialized structures.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

