Efficient replication bypass of size-expanded DNA base pairs in bacterial cells
- PMID: 19444841
- PMCID: PMC3434874
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.200805683
Efficient replication bypass of size-expanded DNA base pairs in bacterial cells
Abstract
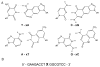
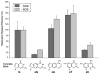
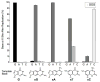
Supersize me! Size-expanded DNA bases (xDNA) are able to encode natural DNA sequences in replication. In vitro experiments with a DNA polymerase show nucleotide incorporation opposite the xDNA bases with correct pairing. In vivo experiments using E. coli show that two xDNA bases (xA and xC, see picture) encode the correct replication partners.
Figures
References
-
- Breslow R. Pure Appl Chem. 1998;70:267–270.
- Kool ET, Waters ML. Nat Chem Biol. 2007;3:70–73. - PubMed
-
- Murakami A, Blake KR, Miller PS. Biochemistry. 1985;24:4041–4046. - PubMed
- Neilsen PE, Egholm M, Berg RH, Buchardt O. Science. 1991;254:1497–1500. - PubMed
- Nielsen P, Pfundheller HM, Wengel J. Chem Commun. 1997:825–826.
- Lescrinier E, Esnouf R, Schraml J, Busson R, Heus H, Hilbers C, Herdewijn P. Chem Biol. 2000;7:719–731. - PubMed
- Egli M, Pallan PS, Pattanayek R, Wilds CJ, Lubini P, Minasov G, Dobler M, Leumann CJ, Eschenmoser A. J Am Chem Soc. 2006;128:10847–10856. - PubMed
- Schöning K, Scholz P, Guntha S, Wu X, Krishnamurthy R, Eschenmoser A. Science. 2000;290:1347–1351. - PubMed
-
- Chaput JC, Szostak JW. J Am Chem Soc. 2003;125:9274–9275. - PubMed
- Shaw BR, Dobrikov M, Wang X, Wan J, He K, Lin JL, Li P, Rait V, Sergueeva Z, Sergueev D. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003;1002:12–29. - PubMed
- Pochet S, Kaminski PA, Van Aerschot A, Herdewijn P, Marlière P. C R Biol. 2003;326:1175–1184. - PubMed
- Sinha S, Kim PH, Switzer C. J Am Chem Soc. 2004;126:40–41. - PubMed
- Jung KH, Marx A. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2005;62:2080–2091. - PMC - PubMed
- Veedu RN, Vester B, Wengel J. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucl Acids. 2007;26:1207–1210. - PubMed
-
- Piccirilli JA, Krauch T, Moroney SE, Benner SA. Nature. 1990;343:33–37. - PubMed
- Moran S, Ren RXF, Rumney S, Kool ET. J Am Chem Soc. 1997;119:2056–2057. - PMC - PubMed
- Matray TJ, Kool ET. Nature. 1999;399:704–708. - PubMed
- Tae EL, Wu Y, Xia G, Schultz PG, Romesberg FE. J Am Chem Soc. 2001;123:7439–7340. - PubMed
- Parsch J, Engels JW. Nucl Acids Res. 2001;20:815–818. - PubMed
- Weizman H, Tor Y. J Am Chem Soc. 2001;123:3375–3376. - PubMed
- Beuck C, Singh I, Bhattacharya A, Hecker W, Parmar VS, Seitz O, Weinhold E. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2003;42:3958–3960. - PubMed
- Paul N, Nashine VC, Hoops G, Zhang P, Zhou J, Bergstrom DE, Davisson VJ. Chem Biol. 2003;10:815–825. - PubMed
- Henry AA, Romesberg FE. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2003;7:727–733. - PubMed
- Hirao I, Harada Y, Kimoto M, Mitsui T, Fujiwara T, Yokoyama S. J Am Chem Soc. 2004;126:13298–13305. - PubMed
- Zhang X, Lee I, Zhou X, Berdis AJ. J Am Chem Soc. 2006;128:143–149. - PubMed
- Moore CL, Zivkovic A, Engels JW, Kuchta RD. Biochemistry. 2004;43:12367–12374. - PubMed
- Hirao I. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2006;10:622–627. - PubMed
- Zahn A, Leumann CJ. Bioorg Med Chem. 2006;14:6174–6188. - PubMed
- Hwang GT, Romesberg FE. J Am Chem Soc. 2008;130:14872–14882. - PMC - PubMed
- Hirao I, Mitsui T, Kimoto M, Yokoyama S. J Am Chem Soc. 2006;129:15549–15555. - PubMed
- Hikishima S, Minakawa N, Kuramoto K, Fujisawa Y, Ogawa M, Matsuda A. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2005;44:596–598. - PubMed
- Battersby TR, Albalos M, Friesenhahn MJ. Chem Biol. 2007;14:525–531. - PubMed
- Doi Y, Chiba J, Morikawa T, Inouye MJ. J Am Chem Soc. 2008;130:8762–8768. - PubMed
-
- Liu H, Gao J, Lynch SR, Maynard L, Saito D, Kool ET. Science. 2003;302:868–871. - PubMed
- Liu H, Gao J, Maynard L, Saito YD, Kool ET. J Am Chem Soc. 2004;126:1102–1109. - PubMed
- Gao J, Liu H, Kool ET. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2005;44:3118–3122. - PubMed
- Gao J, Liu H, Kool ET. J Am Chem Soc. 2004;126:11826–11831. - PubMed
- Liu H, Lynch SR, Kool ET. J Am Chem Soc. 2004;126:6900–6905. - PubMed
- Lynch SR, Liu H, Gao J, Kool ET. J Am Chem Soc. 2006;128:14704–14711. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

