Effects of CYP2D6 status on harmaline metabolism, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics, and a pharmacogenetics-based pharmacokinetic model
- PMID: 19445902
- PMCID: PMC2728464
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bcp.2009.05.011
Effects of CYP2D6 status on harmaline metabolism, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics, and a pharmacogenetics-based pharmacokinetic model
Abstract
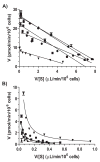
Harmaline is a beta-carboline alkaloid showing neuroprotective and neurotoxic properties. Our recent studies have revealed an important role for cytochrome P450 2D6 (CYP2D6) in harmaline O-demethylation. This study, therefore, aimed to delineate the effects of CYP2D6 phenotype/genotype on harmaline metabolism, pharmacokinetics (PK) and pharmacodynamics (PD), and to develop a pharmacogenetics mechanism-based compartmental PK model. In vitro kinetic studies on metabolite formation in human CYP2D6 extensive metabolizer (EM) and poor metabolizer (PM) hepatocytes indicated that harmaline O-demethylase activity (V(max)/K(m)) was about 9-fold higher in EM hepatocytes. Substrate depletion showed mono-exponential decay trait, and estimated in vitro harmaline clearance (CL(int), microL/min/10(6)cells) was significantly lower in PM hepatocytes (28.5) than EM hepatocytes (71.1). In vivo studies in CYP2D6-humanized and wild-type mouse models showed that wild-type mice were subjected to higher and longer exposure to harmaline (5 and 15mg/kg; i.v. and i.p.), and more severe hypothermic responses. The PK/PD data were nicely described by our pharmacogenetics-based PK model involving the clearance of drug by CYP2D6 (CL(CYP2D6)) and other mechanisms (CL(other)), and an indirect response PD model, respectively. Wild-type mice were also more sensitive to harmaline in marble-burying tests, as manifested by significantly lower ED(50) and steeper Hill slope. These findings suggest that distinct CYP2D6 status may cause considerable variations in harmaline metabolism, PK and PD. In addition, the pharmacogenetics-based PK model may be extended to define PK difference caused by other polymorphic drug-metabolizing enzyme in different populations.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Effects of monoamine oxidase inhibitor and cytochrome P450 2D6 status on 5-methoxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine metabolism and pharmacokinetics.Biochem Pharmacol. 2010 Jul 1;80(1):122-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2010.02.020. Epub 2010 Mar 3. Biochem Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20206139 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacokinetic interactions between monoamine oxidase A inhibitor harmaline and 5-methoxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine, and the impact of CYP2D6 status.Drug Metab Dispos. 2013 May;41(5):975-86. doi: 10.1124/dmd.112.050724. Epub 2013 Feb 7. Drug Metab Dispos. 2013. PMID: 23393220 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of individual cytochrome P450 isozymes to the O-demethylation of the psychotropic beta-carboline alkaloids harmaline and harmine.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2003 Apr;305(1):315-22. doi: 10.1124/jpet.102.047050. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2003. PMID: 12649384
-
Psychedelic 5-methoxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine: metabolism, pharmacokinetics, drug interactions, and pharmacological actions.Curr Drug Metab. 2010 Oct;11(8):659-66. doi: 10.2174/138920010794233495. Curr Drug Metab. 2010. PMID: 20942780 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polymorphism of human cytochrome P450 2D6 and its clinical significance: Part I.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2009;48(11):689-723. doi: 10.2165/11318030-000000000-00000. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2009. PMID: 19817501 Review.
Cited by
-
Integrated network pharmacology and transcriptomics to reveal the mechanism of Passiflora against depressive disorder: An observational study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Oct 11;103(41):e39309. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000039309. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39465851 Free PMC article.
-
Potent inhibition of human organic cation transporter 2 (hOCT2) by β-carboline alkaloids.Xenobiotica. 2017 Dec;47(12):1112-1120. doi: 10.1080/00498254.2016.1271160. Epub 2017 Mar 2. Xenobiotica. 2017. PMID: 27977936 Free PMC article.
-
Modification of 5-methoxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine-induced hyperactivity by monoamine oxidase A inhibitor harmaline in mice and the underlying serotonergic mechanisms.Pharmacol Rep. 2016 Jun;68(3):608-15. doi: 10.1016/j.pharep.2016.01.008. Epub 2016 Feb 5. Pharmacol Rep. 2016. PMID: 26977821 Free PMC article.
-
Human CYP2D6 in the Brain Is Protective Against Harmine-Induced Neurotoxicity: Evidence from Humanized CYP2D6 Transgenic Mice.Mol Neurobiol. 2020 Nov;57(11):4608-4621. doi: 10.1007/s12035-020-02050-w. Epub 2020 Aug 6. Mol Neurobiol. 2020. PMID: 32761352 Free PMC article.
-
Potentiation of 5-methoxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine-induced hyperthermia by harmaline and the involvement of activation of 5-HT1A and 5-HT2A receptors.Neuropharmacology. 2015 Feb;89:342-51. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2014.10.013. Neuropharmacology. 2015. PMID: 25446678 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yu AM, Idle JR, Gonzalez FJ. Polymorphic cytochrome P450 2D6: humanized mouse model and endogenous substrates. Drug Metab Rev. 2004;36(2):243–77. - PubMed
-
- Zanger UM, Raimundo S, Eichelbaum M. Cytochrome P450 2D6: overview and update on pharmacology, genetics, biochemistry. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2004;369(1):23–37. - PubMed
-
- Sellers EM, Tyndale RF. Mimicking gene defects to treat drug dependence. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000;909:233–46. - PubMed
-
- Maurer HH, Kraemer T, Springer D, Staack RF. Chemistry, pharmacology, toxicology, and hepatic metabolism of designer drugs of the amphetamine (ecstasy), piperazine, and pyrrolidinophenone types: a synopsis. Ther Drug Monit. 2004;26(2):127–31. - PubMed
-
- Theobald DS, Maurer HH. Identification of monoamine oxidase and cytochrome P450 isoenzymes involved in the deamination of phenethylamine-derived designer drugs (2C-series) Biochem Pharmacol. 2007;73(2):287–97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

