HIV protease inhibitor lopinavir-induced TNF-alpha and IL-6 expression is coupled to the unfolded protein response and ERK signaling pathways in macrophages
- PMID: 19447225
- PMCID: PMC2704357
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bcp.2009.03.022
HIV protease inhibitor lopinavir-induced TNF-alpha and IL-6 expression is coupled to the unfolded protein response and ERK signaling pathways in macrophages
Abstract
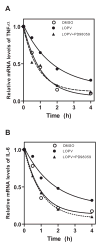
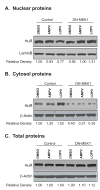
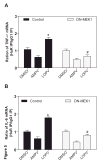
HIV protease inhibitor (PI)-associated cardiovascular risk, especially atherosclerosis, has become a major concern in the clinic. Macrophages are key players in the inflammatory response and atherosclerosis formation. We have previously shown that HIV PIs induce endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, activate the unfolded protein response (UPR), and increase the synthesis of the inflammatory cytokines, TNF-alpha and IL-6, by regulating the intracellular translocation of RNA binding protein HuR in macrophages. However, the underlying signaling mechanisms remain unclear. We show here that the HIV PI lopinavir significantly activated the extracellular-signal regulated protein kinase (ERK), but not c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and p38 MAPK. Lopinavir-induced cytosolic translocation of HuR and TNF-alpha and IL-6 synthesis was attenuated by specific chemical inhibitor of MEK (PD98058) or over-expression of dominant negative mutant of MEK1. In addition, we demonstrated that lopinavir-induced ERK activation and TNF-alpha and IL-6 expression were completely inhibited in macrophages from CHOP null mice. Taken together, these results indicate activation of the UPR plays an essential role in HIV PI-induced inflammatory cytokine synthesis and release by activating ERK, which increases the cytosolic translocation of HuR and subsequent binding to the 3'UTR of TNF-alpha and IL-6 mRNAs in macrophages.
Figures




References
-
- Flexner C. HIV-protease inhibitors. NEnglJMed. 1998;338:1281–92. - PubMed
-
- Bruno R, Sacchi P, Maiocchi L, Patruno S, Filice G. Hepatotoxicity and antiretroviral therapy with protease inhibitors: A review. DigLiver Dis. 2006;38:363–73. - PubMed
-
- Calza L, Manfredi R, Chiodo F. Dyslipidaemia associated with antiretroviral therapy in HIV-infected patients. JAntimicrobChemother. 2004;53:10–4. - PubMed
-
- Martinez E, Domingo P, Galindo MJ, Milinkovic A, Arroyo JA, Baldovi F, et al. Risk of metabolic abnormalities in patients infected with HIV receiving antiretroviral therapy that contains lopinavir-ritonavir. ClinInfectDis. 2004;38:1017–23. - PubMed
-
- Nolan D, Watts GF, Herrmann SE, French MA, John M, Mallal S. Endothelial function in HIV-infected patients receiving protease inhibitor therapy: does immune competence affect cardiovascular risk? QJM. 2003;96:825–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

