Social interactions and 50 kHz ultrasonic vocalizations in adolescent and adult rats
- PMID: 19447288
- PMCID: PMC2684866
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbr.2009.03.025
Social interactions and 50 kHz ultrasonic vocalizations in adolescent and adult rats
Abstract
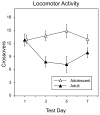
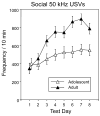
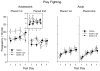
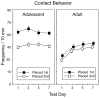
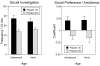
Human adolescents drink partly to facilitate their social interactions, a social facilitatory effect of ethanol also seen in adolescent rats tested under familiar test circumstances. To explore the role of hedonic affect in ethanol-induced social facilitation, this study assessed 50 kHz ultrasonic vocalizations (USVs) in pair-housed adolescent (P29-37) and adult (P71-79) Sprague-Dawley male rats during social interactions. On each of eight test days, animals were socially isolated for 3 h and then injected intraperitoneally with 0 (saline), 0.25 or 0.5 g/kg ethanol. Twenty-five minutes later they were placed alone in a familiar test chamber for a 5-min period, followed by a 10-min encounter with a similarly injected peer. USVs were recorded during this 10-min period, while social interactions were videotaped for later scoring. BECs were measured immediately post-test on day 8. Although the 0.25 g/kg dose of ethanol facilitated play fighting in adolescents but not adults, ethanol had little to no effect on 50 kHz USV production under these test circumstances. USV production was higher in adults than adolescents, despite adolescents consistently engaging in more social behavior. To the extent that 50 kHz USVs index the hedonic value of social interactions, these findings support the conclusion that elevations in social behavior normally evident in adolescents may not be related to increases in hedonic sensitivity for social stimuli.
Figures
References
-
- Beck KH, Thombs DL, Summons TG. The social context of drinking scales: Construct validation and relationship to indicants of abuse in an adolescent population. Addict Behav. 1993;18(2):159–169. - PubMed
-
- Beck KH, Treiman KA. The relationship of social context of drinking, perceived social norms, and parental influence to various drinking patterns of adolescents. Addict Behav. 1996;21(5):633–644. - PubMed
-
- Blanchard RJ, Blanchard DC. Aggressive behavior in the rat. Behav Biol. 1977;21(2):197–224. - PubMed
-
- Blanchard RJ, Blanchard DC, Agullana R, Weiss SM. Twenty-two khz alarm cries to presentation of a predator, by laboratory rats living in visible burrow systems. Physiol Behav. 1991;50(5):967–972. - PubMed
-
- Blanchard RJ, Yudko EB, Blanchard DC, Taukulis HK. High-frequency (35–70 khz) ultrasonic vocalizations in rats confronted with anesthetized conspecifics: Effects of gepirone, ethanol, and diazepam. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1993;44(2):313–319. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

