Spatial distribution, kinetics, signaling and cytokine production during homeostasis driven proliferation of CD4+ T cells
- PMID: 19447493
- PMCID: PMC3090723
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molimm.2009.04.019
Spatial distribution, kinetics, signaling and cytokine production during homeostasis driven proliferation of CD4+ T cells
Abstract
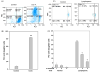
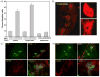
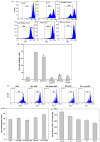
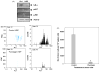
During recovery from lymphopenia, the naïve T-cells undergo homeostasis driven proliferation (HDP) and acquire a memory phenotype. The HDP of T-cells requires signals derived from T-cell-receptor, p56lck kinase, IL-7R and IL-15R. However, the role of other signaling molecules during HDP of CD4+ T-cells remains speculative. The differentiation of naïve T-cells into Th1/Th2/Th17 or Treg populations during HDP is not well understood. Present report describes the spatial and signaling characteristics of HDP of CD4+ T-cells and their cytokine profiles. The HDP of CD4+ T-cells was found to occur only in specific areas (T-cell zones) of secondary lymphoid organs of lymphopenic mice. The inhibitors of MEK and PKC and their combination with inhibitors of PI3kinase and mTOR suppressed mitogen induced T-cell proliferation without affecting their HDP. The CD4+ T-cells taken from reconstituted lymphopenic mice showed activation of proteins involved in NF-kappaB pathway, significantly higher production of pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-6, and lower production of IL-4 as compared to T-cells from normal mice. Plumbagin, a known NF-kappaB blocker inhibited survival as well as HDP of CD4+ T-cells and IL-6 production in activated T-cells. Our results demonstrate the essential role of NF-kappaB during HDP of T-cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Differential modulation of mitogen driven proliferation and homeostasis driven proliferation of T cells by rapamycin, Ly294002 and chlorophyllin.Mol Immunol. 2007 Apr;44(11):2831-40. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2007.01.021. Epub 2007 Feb 26. Mol Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17327134
-
Different competitive capacities of Stat4- and Stat6-deficient CD4+ T cells during lymphophenia-driven proliferation.J Immunol. 2005 Feb 1;174(3):1178-87. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.174.3.1178. J Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15661871
-
CTLA-4 is required by CD4+CD25+ Treg to control CD4+ T-cell lymphopenia-induced proliferation.Eur J Immunol. 2009 Jun;39(6):1544-51. doi: 10.1002/eji.200838603. Eur J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19462377 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous proliferation: burst-like CD4 T cell proliferation in lymphopenic settings.Semin Immunol. 2005 Jun;17(3):201-7. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2005.02.005. Semin Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15826825 Review.
-
Memories are made of this: synergy of T cell receptor and cytokine signals in CD4(+) central memory cell survival.Trends Immunol. 2007 Jun;28(6):245-8. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2007.04.006. Epub 2007 Apr 25. Trends Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17462952 Review.
Cited by
-
Plumbagin inhibits proliferative and inflammatory responses of T cells independent of ROS generation but by modulating intracellular thiols.J Cell Biochem. 2010 Aug 1;110(5):1082-93. doi: 10.1002/jcb.22620. J Cell Biochem. 2010. PMID: 20564204 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative stress via inhibition of the mitochondrial electron transport and Nrf-2-mediated anti-oxidative response regulate the cytotoxic activity of plumbagin.Sci Rep. 2018 Jan 18;8(1):1073. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-19261-w. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29348410 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agrawal A, Dillon S, Denning TL, Pulendran B. ERK1−/− mice exhibit Th1 cell polarization and increased susceptibility to experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Immunol. 2006;176:5788–5796. - PubMed
-
- Baccala R, Theofilopoulos AN. The new paradigm of T-cell homeostatic proliferation-induced autoimmunity. Trends Immunol. 2005;26:5–8. - PubMed
-
- Baier G, Telford D, Giampa L, Coggeshall KM, Baier-Bitterlich G, Isakov N, Altman A. Molecular cloning and characterization of PKC theta, a novel member of the protein kinase C (PKC) gene family expressed predominantly in hematopoietic cells. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:4997–5004. - PubMed
-
- Ernst B, Lee DS, Chang JM, Sprent J, Surh CD. The peptide ligands mediating positive selection in the thymus control T cell survival and homeostatic proliferation in the periphery. Immunity. 1999;11:173–181. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

