Hierarchical hidden Markov model with application to joint analysis of ChIP-chip and ChIP-seq data
- PMID: 19447789
- PMCID: PMC2732365
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp312
Hierarchical hidden Markov model with application to joint analysis of ChIP-chip and ChIP-seq data
Abstract
Motivation: Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) experiments followed by array hybridization, or ChIP-chip, is a powerful approach for identifying transcription factor binding sites (TFBS) and has been widely used. Recently, massively parallel sequencing coupled with ChIP experiments (ChIP-seq) has been increasingly used as an alternative to ChIP-chip, offering cost-effective genome-wide coverage and resolution up to a single base pair. For many well-studied TFs, both ChIP-seq and ChIP-chip experiments have been applied and their data are publicly available. Previous analyses have revealed substantial technology-specific binding signals despite strong correlation between the two sets of results. Therefore, it is of interest to see whether the two data sources can be combined to enhance the detection of TFBS.
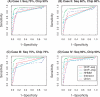
Results: In this work, hierarchical hidden Markov model (HHMM) is proposed for combining data from ChIP-seq and ChIP-chip. In HHMM, inference results from individual HMMs in ChIP-seq and ChIP-chip experiments are summarized by a higher level HMM. Simulation studies show the advantage of HHMM when data from both technologies co-exist. Analysis of two well-studied TFs, NRSF and CCCTC-binding factor (CTCF), also suggests that HHMM yields improved TFBS identification in comparison to analyses using individual data sources or a simple merger of the two.
Availability: Source code for the software ChIPmeta is freely available for download at http://www.umich.edu/~hwchoi/HHMMsoftware.zip, implemented in C and supported on linux.
Figures

References
-
- Barski A, et al. High-resolution profiling of histone methylations in the human genome. Cell. 2007;129:823–837. - PubMed
-
- Bui H, et al. Proceedings of AAAI. San Jose, CA: 2004. Hierarchical hidden Markov models with general state hierarchy.
-
- Cartharius K, et al. Matinspector and beyond: promoter analysis based on transcription factor binding sites. Bioinformatics. 2005;21:2933–2942. - PubMed
-
- Chen X, et al. Integration of external signaling pathways with the core transcriptional network in embryonic stem cells. Cell. 2008;133:1106–1117. - PubMed

