RsmC of Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora negatively controls motility, extracellular protein production, and virulence by binding FlhD and modulating transcriptional activity of the master regulator, FlhDC
- PMID: 19447906
- PMCID: PMC2704716
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00154-09
RsmC of Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora negatively controls motility, extracellular protein production, and virulence by binding FlhD and modulating transcriptional activity of the master regulator, FlhDC
Erratum in
-
Correction for Chatterjee et al., RsmC of Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora Negatively Controls Motility, Extracellular Protein Production, and Virulence by Binding FlhD and Modulating Transcriptional Activity of the Master Regulator, FlhDC.J Bacteriol. 2015 Dec;197(24):3848. doi: 10.1128/JB.00735-15. J Bacteriol. 2015. PMID: 26581822 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
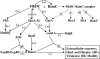
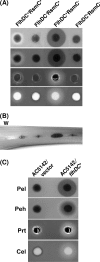
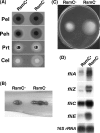
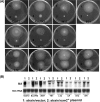
RsmC and FlhDC are global regulators controlling extracellular proteins/enzymes, rsmB RNA, motility, and virulence of Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora. FlhDC, the master regulator of flagellar genes, controls these traits by positively regulating gacA, fliA, and rsmC and negatively regulating hexA. RsmC, on the other hand, is a negative regulator of extracellular proteins/enzymes, motility, and virulence since the deficiency of RsmC in FlhDC(+) strain results in overproduction of extracellular proteins/enzymes, hypermotility, and hypervirulence. These phenotypes are abolished in an RsmC(-) FlhDC(-) double mutant. We show that RsmC interferes with FlhDC action. Indeed, the expression of all three targets (i.e., gacA, rsmC, and fliA) positively regulated in E. carotovora subsp. carotovora by FlhDC is inhibited by RsmC. RsmC also partly relieves the inhibition of hexA expression by FlhDC. The results of yeast two-hybrid analysis revealed that RsmC binds FlhD and FlhDC, but not FlhC. We propose that binding of RsmC with FlhD/FlhDC interferes with its regulatory functions and that RsmC acts as an anti-FlhD(4)FlhC(2) factor. We document here for the first time that RsmC interferes with activation of fliA and motility in several members of the Enterobacteriaceae family. The extent of E. carotovora subsp. carotovora RsmC-mediated inhibition of FlhDC-dependent expression of fliA and motility varies depending upon enterobacterial species. The data presented here support the idea that differences in structural features in enterobacterial FlhD are responsible for differential susceptibility to E. carotovora subsp. carotovora RsmC action.
Figures


References
-
- Aizawa, S. I., and T. Kubori. 1998. Bacterial flagellation and cell division. Genes Cells. 3625-634. - PubMed
-
- Aldridge, P., and K. T. Hughes. 2002. Regulation of flagellar assembly. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 5160-165. - PubMed
-
- Barembruch, C., and R. Hengge. 2007. Cellular levels and activity of the flagellar sigma factor FliA of Escherichia coli are controlled by FlgM-modulated proteolysis. Mol. Microbiol. 6576-89. - PubMed
-
- Barras, F., F. Van Gijsegem, and A. K. Chatterjee. 1994. Extracellular enzymes and pathogenesis of soft-rot Erwinia. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 32201-234.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

