Vacuolar-type proton pumps in insect epithelia
- PMID: 19448071
- PMCID: PMC2683008
- DOI: 10.1242/jeb.030007
Vacuolar-type proton pumps in insect epithelia
Abstract
Active transepithelial cation transport in insects was initially discovered in Malpighian tubules, and was subsequently also found in other epithelia such as salivary glands, labial glands, midgut and sensory sensilla. Today it appears to be established that the cation pump is a two-component system of a H(+)-transporting V-ATPase and a cation/nH(+) antiporter. After tracing the discovery of the V-ATPase as the energizer of K(+)/nH(+) antiport in the larval midgut of the tobacco hornworm Manduca sexta we show that research on the tobacco hornworm V-ATPase delivered important findings that emerged to be of general significance for our knowledge of V-ATPases, which are ubiquitous and highly conserved proton pumps. We then discuss the V-ATPase in Malpighian tubules of the fruitfly Drosophila melanogaster where the potential of post-genomic biology has been impressively illustrated. Finally we review an integrated physiological approach in Malpighian tubules of the yellow fever mosquito Aedes aegypti which shows that the V-ATPase delivers the energy for both transcellular and paracellular ion transport.
Figures
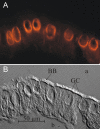
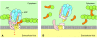

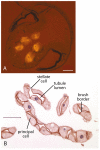
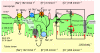
References
-
- Al Awqati, Q. (1978). H+ transport in urinary epithelia. Am. J. Physiol. 235, F77-F88. - PubMed
-
- Allan, A. K., Du, J., Davies, S. A. and Dow, J. A. (2005). Genome-wide survey of V-ATPase genes in Drosophila reveals a conserved renal phenotype for lethal alleles. Physiol. Genomics 22, 128-138. - PubMed
-
- Azuma, M., Harvey, W. R. and Wieczorek, H. (1995). Stoichiometry of K+/H+ antiport helps to explain extracellular pH 11 in a model epithelium. FEBS Lett. 361, 153-156. - PubMed
-
- Bertram, G. and Wessing, A. (1994). Intracellular pH regulation by the plasma membrane V-ATPase in Malpighian tubules of Drosophila larvae. J. Comp. Physiol. B 164, 238-246. - PubMed
-
- Bertram, G., Schleithoff, L., Zimmermann, P. and Wessing, A. (1991). Bafilomycin A1 is a potent inhibitor of urine formation by Malpighian tubules of Drosophila hydei: is a vacuolar-type ATPase involved in ion and fluid secretion? J. Insect Physiol. 37, 201-209.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

