Myocardial TLR4 is a determinant of neutrophil infiltration after global myocardial ischemia: mediating KC and MCP-1 expression induced by extracellular HSC70
- PMID: 19448144
- PMCID: PMC2711729
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00292.2009
Myocardial TLR4 is a determinant of neutrophil infiltration after global myocardial ischemia: mediating KC and MCP-1 expression induced by extracellular HSC70
Abstract
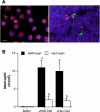
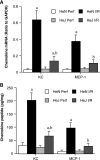
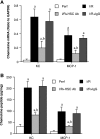
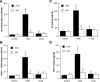
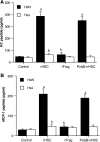
Cardiac surgery with global myocardial ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) induces a myocardial inflammatory response that impairs cardiac recovery. Chemokines contribute to the overall myocardial inflammatory response through inducing leukocyte infiltration. Although Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) has an important role in postischemic myocardial injury, the relative roles of myocardial tissue and leukocyte TLR4 in leukocyte infiltration, as well as the role of TLR4 in myocardial chemokine expression, are unclear. Our recent study, in an isolated mouse heart model of global I/R, found that the 70-kDa heat shock cognate protein (HSC70) is released from cardiac cells and mediates the expression of cardiodepressant cytokines via a TLR4-dependent mechanism. In the present study, we tested the hypotheses that myocardial tissue TLR4 has a major role in mediating neutrophil infiltration and that myocardial TLR4 and extracellular HSC70 contribute to the mechanisms underlying cardiac chemokine response to global I/R. We subjected hearts isolated from TLR4-defective and TLR4-competent mice to global I/R and examined myocardial neutrophil infiltration and expression of keratinocyte-derived chemokine (KC) and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1). TLR4-defective hearts exhibited reduced neutrophil infiltration regardless of the phenotypes of neutrophils perfused during reperfusion and expressed lower levels of KC and MCP-1. HSC70-specific antibody reduced myocardial expression of KC and MCP-1 after I/R. Furthermore, perfusion of HSC70 increased KC and MCP-1 expression in TLR4-competent hearts but not in TLR4-defective hearts, and HSC70 also induced the chemokine response in macrophages in a TLR4-dependent fashion. A recombinant HSC70 fragment lacking the substrate-binding domain was insufficient to induce chemokine expression in hearts and cells. This study demonstrates that myocardial tissue TLR4, rather than neutrophil TLR4, is the determinant of myocardial neutrophil infiltration after global I/R. TLR4 mediates myocardial chemokine expression, and the mechanisms involve extracellular HSC70. These results imply the HSC70-TLR4 interaction as a novel mechanism underlying the myocardial chemokine response to global I/R.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Human myocardium releases heat shock protein 27 (HSP27) after global ischemia: the proinflammatory effect of extracellular HSP27 through toll-like receptor (TLR)-2 and TLR4.Mol Med. 2014 Jun 9;20(1):280-9. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2014.00058. Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 24918749 Free PMC article.
-
Critical role of extracellular heat shock cognate protein 70 in the myocardial inflammatory response and cardiac dysfunction after global ischemia-reperfusion.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2008 Jun;294(6):H2805-13. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00299.2008. Epub 2008 Apr 25. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18441202 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-like receptor 4 mediates the inflammatory responses and matrix protein remodeling in remote non-ischemic myocardium in a mouse model of myocardial ischemia and reperfusion.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 30;10(3):e0121853. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0121853. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25823011 Free PMC article.
-
The inflammatory response in myocardial infarction.Cardiovasc Res. 2002 Jan;53(1):31-47. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6363(01)00434-5. Cardiovasc Res. 2002. PMID: 11744011 Review.
-
Chemokines in ischemia and reperfusion.Thromb Haemost. 2007 May;97(5):738-47. Thromb Haemost. 2007. PMID: 17479184 Review.
Cited by
-
Gender disparity in the role of TLR2 in post-ischemic myocardial inflammation and injury.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015 Jul 15;8(7):10537-47. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 26379843 Free PMC article.
-
Human myocardium releases heat shock protein 27 (HSP27) after global ischemia: the proinflammatory effect of extracellular HSP27 through toll-like receptor (TLR)-2 and TLR4.Mol Med. 2014 Jun 9;20(1):280-9. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2014.00058. Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 24918749 Free PMC article.
-
Myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury: from basic science to clinical bedside.Semin Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2012 Sep;16(3):123-32. doi: 10.1177/1089253211436350. Epub 2012 Feb 23. Semin Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2012. PMID: 22368166 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A hepatic protein, fetuin-A, occupies a protective role in lethal systemic inflammation.PLoS One. 2011 Feb 8;6(2):e16945. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016945. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21347455 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidized low density lipoprotein induces bone morphogenetic protein-2 in coronary artery endothelial cells via Toll-like receptors 2 and 4.J Biol Chem. 2011 Apr 8;286(14):12213-20. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.214619. Epub 2011 Feb 16. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21325271 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson RL, Wang CY, vanKersen I, Lee KJ, Welch WJ, Lavagnini P, Hahn GM. An immunoassay for heat shock protein 73/72: use of the assay to correlate HSP73/72 levels in mammalian cells with heat response. Int J Hyperthermia 9: 539–552, 1993. - PubMed
-
- Anselmi A, Abbate A, Girola F, Nasso G, Biondi-Zoccai GG, Possati G, Gaudino M. Myocardial ischemia, stunning, inflammation, and apoptosis during cardiac surgery: a review of evidence. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 25: 304–311, 2004. - PubMed
-
- Asehnoune K, Strassheim D, Mitra S, Kim JY, Abraham E. Involvement of reactive oxygen species in Toll-like receptor 4-dependent activation of NF-kappa B. J Immunol 172: 2522–2529, 2004. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Abraham R, Weinbroum AA, Dekel B, Paret G. Chemokines and the inflammatory response following cardiopulmonary bypass—a new target for therapeutic intervention? A review. Paediatr Anaesth 13: 655–661, 2003. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

