RAG-1 and ATM coordinate monoallelic recombination and nuclear positioning of immunoglobulin loci
- PMID: 19448632
- PMCID: PMC2693356
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.1735
RAG-1 and ATM coordinate monoallelic recombination and nuclear positioning of immunoglobulin loci
Erratum in
- Nat Immunol. 2009 Jun;10(6). doi: 10.1038/ni.1735 doi: 10.1038/ni.1735
- Nat Immunol. 2009 Sep;10(9):1034
- Nat Immunol. 2010 Mar;11(4):355-6
Abstract
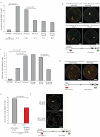
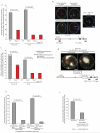
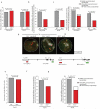
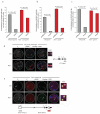
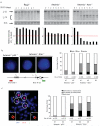
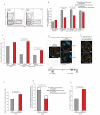
Coordinated recombination of homologous antigen receptor loci is thought to be important for allelic exclusion. Here we show that homologous immunoglobulin alleles pair in a stage-specific way that mirrors the recombination patterns of these loci. The frequency of homologous immunoglobulin pairing was much lower in the absence of the RAG-1-RAG-2 recombinase and was restored in Rag1-/- developing B cells with a transgene expressing a RAG-1 active-site mutant that supported DNA binding but not cleavage. The introduction of DNA breaks on one immunoglobulin allele induced ATM-dependent repositioning of the other allele to pericentromeric heterochromatin. ATM activated by the cleaved allele acts in trans on the uncleaved allele to prevent biallelic recombination and chromosome breaks or translocations.
Figures
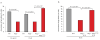

References
-
- Hesslein DG, Schatz DG. Factors and forces controlling V(D)J recombination. Adv Immunol. 2001;78:169–232. - PubMed
-
- Bassing CH, Swat W, Alt FW. The mechanism and regulation of chromosomal V(D)J recombination. Cell. 2002;109(Suppl):S45–55. - PubMed
-
- Hsu LY, et al. A conserved transcriptional enhancer regulates RAG gene expression in developing B cells. Immunity. 2003;19:105–17. - PubMed
-
- Gellert M. V(D)J recombination: RAG proteins, repair factors, and regulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 2002;71:101–32. - PubMed
-
- Roth DB. Restraining the V(D)J recombinase. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003;3:656–66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

