Inhibition of osteoblastic bone formation by nuclear factor-kappaB
- PMID: 19448637
- PMCID: PMC2768554
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.1954
Inhibition of osteoblastic bone formation by nuclear factor-kappaB
Abstract
An imbalance in bone formation relative to bone resorption results in the net bone loss that occurs in osteoporosis and inflammatory bone diseases. Although it is well known how bone resorption is stimulated, the molecular mechanisms that mediate impaired bone formation are poorly understood. Here we show that the time- and stage-specific inhibition of endogenous inhibitor of kappaB kinase (IKK)--nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) in differentiated osteoblasts substantially increases trabecular bone mass and bone mineral density without affecting osteoclast activities in young mice. Moreover, inhibition of IKK-NF-kappaB in differentiated osteoblasts maintains bone formation, thereby preventing osteoporotic bone loss induced by ovariectomy in adult mice. Inhibition of IKK-NF-kappaB enhances the expression of Fos-related antigen-1 (Fra-1), an essential transcription factor involved in bone matrix formation in vitro and in vivo. Taken together, our results suggest that targeting IKK-NF-kappaB may help to promote bone formation in the treatment of osteoporosis and other bone diseases.
Figures
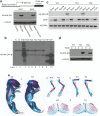
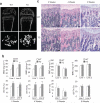

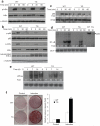

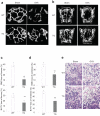
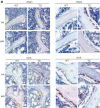

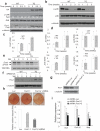

References
-
- Wagner EF, Karsenty G. Genetic control of skeletal development. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2001;11:527–532. - PubMed
-
- Zaidi M. Skeletal remodeling in health and disease. Nat Med. 2007;13:791–801. - PubMed
-
- Zelzer E, Olsen BR. Multiple roles of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in skeletal development, growth, and repair. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2005;65:169–187. - PubMed
-
- Kronenberg HM. Twist Genes Regulate Runx2 and Bone Formation. Dev. Cell. 2004;6:317–318. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

