Rapid creation and quantitative monitoring of high coverage shRNA libraries
- PMID: 19448642
- PMCID: PMC2783737
- DOI: 10.1038/nmeth.1330
Rapid creation and quantitative monitoring of high coverage shRNA libraries
Abstract
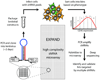
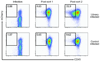
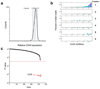
Short hairpin RNA libraries are limited by low efficacy of many shRNAs and by off-target effects, which give rise to false negatives and false positives, respectively. Here we present a strategy for rapidly creating expanded shRNA pools (approximately 30 shRNAs per gene) that are analyzed by deep sequencing (EXPAND). This approach enables identification of multiple effective target-specific shRNAs from a complex pool, allowing a rigorous statistical evaluation of true hits.
Figures
References
-
- Bernards R, Brummelkamp TR, Beijersbergen RL. shRNA libraries and their use in cancer genetics. Nat. Methods. 2006;3:701–706. - PubMed
-
- Chang K, Elledge SJ, Hannon GJ. Lessons from Nature: microRNA-based shRNA libraries. Nat. Methods. 2006;3:707–714. - PubMed
-
- Root DE, Hacohen N, Hahn WC, Lander ES, Sabatini DM. Genome-scale loss-of-function screening with a lentiviral RNAi library. Nat. Methods. 2006;3:715–719. - PubMed
-
- Cleary MA, et al. Production of complex nucleic acid libraries using highly parallel in situ oligonucleotide synthesis. Nat. Methods. 2004;1:241–248. - PubMed
-
- Silva JM, et al. Second-generation shRNA libraries covering the mouse and human genomes. Nat. Genet. 2005;37:1281–1288. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

