Essential role of KLF5 transcription factor in cell proliferation and differentiation and its implications for human diseases
- PMID: 19448973
- PMCID: PMC11115749
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-009-0045-z
Essential role of KLF5 transcription factor in cell proliferation and differentiation and its implications for human diseases
Abstract
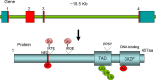
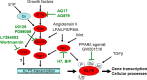
KLF5 (Kruppel-like factor 5) is a basic transcription factor binding to GC boxes at a number of gene promoters and regulating their transcription. KLF5 is expressed during development and, in adults, with higher levels in proliferating epithelial cells. The expression and activity of KLF5 are regulated by multiple signaling pathways, including Ras/MAPK, PKC, and TGFbeta, and various posttranslational modifications, including phosphorylation, acetylation, ubiquitination, and sumoylation. Consistently, KLF5 mediates the signaling functions in cell proliferation, cell cycle, apoptosis, migration, differentiation, and stemness by regulating gene expression in response to environment stimuli. The expression of KLF5 is frequently abnormal in human cancers and in cardiovascular disease-associated vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs). Due to its significant functions in cell proliferation, survival, and differentiation, KLF5 could be a potential diagnostic biomarker and therapeutic target for cancer and cardiovascular diseases.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

