Single and combined effects of alphavbeta3- and alpha5beta1-integrins on capillary tube formation in a human fibrinous matrix
- PMID: 19449108
- PMCID: PMC2752504
- DOI: 10.1007/s10456-009-9150-8
Single and combined effects of alphavbeta3- and alpha5beta1-integrins on capillary tube formation in a human fibrinous matrix
Abstract
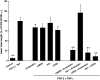
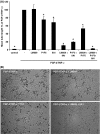
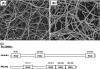
The fibrinous exudate of a wound or tumor stroma facilitates angiogenesis. We studied the involvement of RGD-binding integrins during tube formation in human plasma-derived fibrin clots and human purified fibrin matrices. Capillary-like tube formation by human microvascular endothelial cells in a 3D plasma-derived fibrinous matrix was induced by FGF-2 and TNF-alpha and depended largely on cell-bound u-PA and plasmin activities. While tube formation was minimally affected by the addition of either the alphavbeta3-integrin inhibiting mAb LM609 or the alpha5-integrin inhibiting mAb IIA1, the general RGD-antagonist echistatin completely inhibited this process. Remarkably, when alphavbeta3- and alpha5beta1-integrins were inhibited simultaneously, tube formation was reduced by 78%. It was accompanied by a 44% reduction of u-PA antigen accumulation and 41% less production of fibrin degradation products. alphavbeta5-integrin-blocking antibodies further enhanced the inhibition by mAb LM609 and mAb IIA1 to 94%, but had no effect by themselves. alphav-specific cRGD only inhibited angiogenesis when alpha5beta1-integrin was simultaneously blocked. Endostatin mimicked the effect of alpha5beta1-integrin and inhibited tube formation only in the presence of LM609 or cRGD (73 and 80%, respectively). Comparable results were obtained when purified fibrin matrices were used instead of the plasma-derived fibrinous matrices. These data show that blocking of tube formation in a fibrinous exudate requires the simultaneous inhibition of alphavbeta3- and alpha5beta1-integrins. This may bear impact on attempts to influence angiogenesis in a fibrinous environment.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Role and localization of urokinase receptor in the formation of new microvascular structures in fibrin matrices.Am J Pathol. 1999 Jun;154(6):1731-42. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65429-6. Am J Pathol. 1999. PMID: 10362798 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of steroid hormones and retinoids on the formation of capillary-like tubular structures of human microvascular endothelial cells in fibrin matrices is related to urokinase expression.Blood. 1998 Aug 1;92(3):927-38. Blood. 1998. PMID: 9680361
-
A novel RGD antagonist that targets both alphavbeta3 and alpha5beta1 induces apoptosis of angiogenic endothelial cells on type I collagen.Vascul Pharmacol. 2003 Feb;40(2):77-89. doi: 10.1016/s1537-1891(02)00339-7. Vascul Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12646396
-
Anti-angiogenic cancer therapy based on integrin alphavbeta3 antagonism.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2006 Sep;6(5):407-28. doi: 10.2174/187152006778226530. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2006. PMID: 17017851 Review.
-
Role of fibrin matrix in angiogenesis.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001;936:426-37. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2001.tb03526.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001. PMID: 11460496 Review.
Cited by
-
Scaffold Chemical Model Based on Collagen-Methyl Methacrylate Graft Copolymers.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Jun 8;15(12):2618. doi: 10.3390/polym15122618. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37376264 Free PMC article.
-
Transformed MDCK cells secrete elevated MMP1 that generates LAMA5 fragments promoting endothelial cell angiogenesis.Sci Rep. 2016 Jun 21;6:28321. doi: 10.1038/srep28321. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27324842 Free PMC article.
-
Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Marine Collagen and Fibrinogen Proteins in the Presence of Thrombin.Mar Drugs. 2020 Apr 11;18(4):208. doi: 10.3390/md18040208. Mar Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32290502 Free PMC article.
-
Integrins in Cardiovascular Health and Disease: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Opportunities.Biomolecules. 2025 Feb 6;15(2):233. doi: 10.3390/biom15020233. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40001536 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrins as therapeutic targets: lessons and opportunities.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2010 Oct;9(10):804-20. doi: 10.1038/nrd3266. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2010. PMID: 20885411 Review.
References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1038/nm0603-653', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1038/nm0603-653'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '12778163', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12778163/'}]}
- Carmeliet P (2003) Angiogenesis in health and disease. Nat Med 9:653–660. doi:10.1038/nm0603-653 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1038/nm0195-27', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1038/nm0195-27'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '7584949', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7584949/'}]}
- Folkman J (1995) Angiogenesis in cancer, vascular, rheumatoid and other disease. Nat Med 1:27–31. doi:10.1038/nm0195-27 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '3537791', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3537791/'}]}
- Dvorak HF (1986) Tumors: wounds that do not heal similarities between tumor stroma generation and wound healing. N Engl J Med 315:1650–1659 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '11460496', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11460496/'}]}
- van Hinsbergh VWM, Collen A, Koolwijk P (2001) Role of fibrin matrix in angiogenesis. Ann N Y Acad Sci 936:426–437 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1200/JCO.2002.10.088', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2002.10.088'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '12409337', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12409337/'}]}
- Dvorak HF (2002) Vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor: a critical cytokine in tumor angiogenesis and a potential target for diagnosis and therapy. J Clin Oncol 20:4368–4380. doi:10.1200/JCO.2002.10.088 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

