EGFR-targeted diphtheria toxin stimulates TRAIL killing of glioblastoma cells by depleting anti-apoptotic proteins
- PMID: 19449148
- PMCID: PMC3811048
- DOI: 10.1007/s11060-009-9914-4
EGFR-targeted diphtheria toxin stimulates TRAIL killing of glioblastoma cells by depleting anti-apoptotic proteins
Abstract
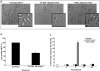
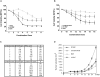
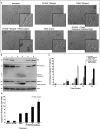
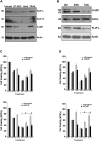
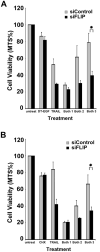
Current treatments for Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) involve surgery, radiotherapy, and cytotoxic chemotherapy; however, these treatments are not effective and there is an urgent need for better treatments. We investigated GBM cell killing by a novel drug combination involving DT-EGF, an Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-targeted bacterial toxin, and Tumor Necrosis Factor-Related Apoptosis Inducing Ligand (TRAIL) or antibodies that activate the TRAIL receptors DR4 and DR5. DT-EGF kills GBM cells by a non apoptotic mechanism whereas TRAIL kills by inducing apoptosis. GBM cells treated with DT-EGF and TRAIL were killed in a synergistic fashion in vitro and the combination was more effective than either treatment alone in vivo. Tumor cell death with the combination occurred by caspase activation and apoptosis due to DT-EGF positively regulating TRAIL killing by depleting FLIP, a selective inhibitor of TRAIL receptor-induced apoptosis. These data provide a mechanism-based rationale for combining targeted toxins and TRAIL receptor agonists to treat GBM.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tanshinone IIA sensitizes TRAIL-induced apoptosis in glioblastoma through inducing the expression of death receptors (and suppressing STAT3 activation).Brain Res. 2021 Sep 1;1766:147515. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2021.147515. Epub 2021 May 11. Brain Res. 2021. PMID: 33984327
-
Therapeutic stem cells expressing variants of EGFR-specific nanobodies have antitumor effects.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Oct 9;109(41):16642-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1202832109. Epub 2012 Sep 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 23012408 Free PMC article.
-
TRAIL and doxorubicin combination enhances anti-glioblastoma effect based on passive tumor targeting of liposomes.J Control Release. 2011 Aug 25;154(1):93-102. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2011.05.008. Epub 2011 May 15. J Control Release. 2011. PMID: 21609741
-
Overcoming TRAIL Resistance for Glioblastoma Treatment.Biomolecules. 2021 Apr 14;11(4):572. doi: 10.3390/biom11040572. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33919846 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current approaches in enhancing TRAIL therapies in glioblastoma.Neurooncol Adv. 2023 Apr 21;5(1):vdad047. doi: 10.1093/noajnl/vdad047. eCollection 2023 Jan-Dec. Neurooncol Adv. 2023. PMID: 37215952 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Novel therapies in glioblastoma.Neurol Res Int. 2012;2012:428565. doi: 10.1155/2012/428565. Epub 2012 Feb 28. Neurol Res Int. 2012. PMID: 22530121 Free PMC article.
-
On the TRAIL to successful cancer therapy? Predicting and counteracting resistance against TRAIL-based therapeutics.Oncogene. 2013 Mar 14;32(11):1341-50. doi: 10.1038/onc.2012.164. Epub 2012 May 14. Oncogene. 2013. PMID: 22580613 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2007. CA Cancer J Clin. 2007;57:43–66. - PubMed
-
- Polednak AP, Flannery JT. Brain, other central nervous system, and eye cancer. Cancer. 1995;75:330–337. - PubMed
-
- Kleihues P, Louis DN, Scheithauer BW, Rorke LB, Reifenberger G, Burger PC, Cavenee WK. The WHO classification of tumors of the nervous system. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2002;61:215–225. discussion 226-219. - PubMed
-
- Thorburn A, Thorburn J, Frankel AE. Induction of apoptosis by tumor cell-targeted toxins. Apoptosis. 2004;9:19–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

