A new function for LAT and CD8 during CD8-mediated apoptosis that is independent of TCR signal transduction
- PMID: 19449311
- PMCID: PMC3049189
- DOI: 10.1002/eji.200839062
A new function for LAT and CD8 during CD8-mediated apoptosis that is independent of TCR signal transduction
Abstract
The majority (>95%) of thymocytes undergo apoptosis during selection in the thymus. Several mechanisms have been proposed to explain how apoptosis of thymocytes that are not positively selected occurs; however, it is unknown whether thymocytes die purely by "neglect" or whether signaling through a cell-surface receptor initiates an apoptotic pathway. We have previously demonstrated that on double positive thymocytes the ligation of CD8 in the absence of TCR engagement results in apoptosis and have postulated this is a mechanism to remove thymocytes that have failed positive selection. On mature single positive T cells CD8 acts as a co-receptor to augment signaling through the TCR that is dependent on the phosphorylation of the adaptor protein, linker for activation of T cells (LAT). Here, we show that during CD8-mediated apoptosis of double positive thymocytes there is an increase in the association of CD8 with LAT and an increase in LAT tyrosine phosphorylation. Decreasing LAT expression and mutation of tyrosine residues of LAT reduced apoptosis upon crosslinking of CD8. Our results identify novel functions for both CD8 and LAT that are independent of TCR signal transduction and suggest a mechanism for signal transduction leading to apoptosis upon CD8 crosslinking.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no commercial or financial conflict of interest.
Figures
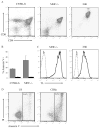
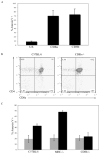

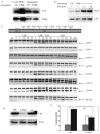
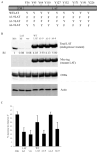
Similar articles
-
Association of the adaptor molecule LAT with CD4 and CD8 coreceptors identifies a new coreceptor function in T cell receptor signal transduction.J Exp Med. 1999 Nov 15;190(10):1517-26. doi: 10.1084/jem.190.10.1517. J Exp Med. 1999. PMID: 10562325 Free PMC article.
-
Perturbed regulation of ZAP-70 and sustained tyrosine phosphorylation of LAT and SLP-76 in c-Cbl-deficient thymocytes.J Immunol. 1999 Jun 15;162(12):7133-9. J Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10358158
-
Control of TCR-mediated activation of beta 1 integrins by the ZAP-70 tyrosine kinase interdomain B region and the linker for activation of T cells adapter protein.J Immunol. 2004 May 1;172(9):5379-87. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.172.9.5379. J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15100278
-
New perspectives on a developmental dilemma: the kinetic signaling model and the importance of signal duration for the CD4/CD8 lineage decision.Curr Opin Immunol. 2002 Apr;14(2):207-15. doi: 10.1016/s0952-7915(02)00323-0. Curr Opin Immunol. 2002. PMID: 11869894 Review.
-
CD4, CD8 and the role of CD45 in T-cell activation.Curr Opin Immunol. 1993 Jun;5(3):334-40. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(93)90050-3. Curr Opin Immunol. 1993. PMID: 8347296 Review.
Cited by
-
MHC class I molecules with Superenhanced CD8 binding properties bypass the requirement for cognate TCR recognition and nonspecifically activate CTLs.J Immunol. 2010 Apr 1;184(7):3357-66. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0902398. Epub 2010 Feb 26. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20190139 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Werlen G, Hausmann B, Naeher D, Palmer E. Signaling life and death in the thymus: timing is everything. Science. 2003;299:1859–1863. - PubMed
-
- Jung KC, Park WS, Kim HJ, Choi EY, Kook MC, Lee HW, Bae Y. TCR-independent and caspase-independent apoptosis of murine thymocytes by CD24 cross-linking. J Immunol. 2004;172:795–802. - PubMed
-
- Lesage S, Steff AM, Philippoussis F, Page M, Trop S, Mateo V, Hugo P. CD4+ CD8+ thymocytes are preferentially induced to die following CD45 cross-linking, through a novel apoptotic pathway. J Immunol. 1997;159:4762–4771. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

