Intracardiac injection of erythropoietin induces stem cell recruitment and improves cardiac functions in a rat myocardial infarction model
- PMID: 19449462
- PMCID: PMC3822874
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2008.00546.x
Intracardiac injection of erythropoietin induces stem cell recruitment and improves cardiac functions in a rat myocardial infarction model
Abstract
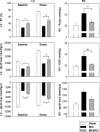
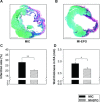
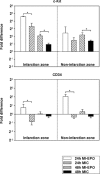
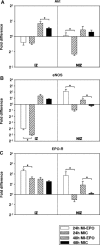
Erythropoietin (EPO) protects the myocardium from ischaemic injury and promotes beneficial remodelling. We assessed the therapeutic efficacy of intracardiac EPO injection and EPO-mediated stem cell homing in a rat myocardial infarction (MI) model. Following MI, EPO (3000 U/kg) or saline was delivered by intracardiac injection. Compared to myocardial infarction control group (MIC), EPO significantly improved left ventricular function (n =11-14, P < 0.05) and decreased right ventricular wall stress (n = 8, P < 0.05) assessed by pressure-volume loops after 6 weeks. MI-EPO hearts exhibited smaller infarction size (20.1 +/- 1.1% versus 27.8 +/- 1.2%; n = 6-8, P < 0.001) and greater capillary density (338.5 +/- 14.7 versus 259.8 +/- 9.2 vessels per mm2; n = 6-8, P < 0.001) than MIC hearts. Direct EPO injection reduced post-MI myocardial apoptosis by approximately 41% (0.27 +/- 0.03% versus 0.42 +/- 0.03%; n = 6, P= 0.005). The chemoattractant SDF-1 was up-regulated significantly assessed by quantitative realtime PCR and immunohistology. c-Kit(+) and CD34(+) stem cells were significantly more numerous in MI-EPO than in MIC at 24 hrs in peripheral blood (n = 7, P < 0.05) and 48 hrs in the infarcted hearts (n = 6, P < 0.001). Further, the mRNAs of Akt, eNOS and EPO receptor were significantly enhanced in MI-EPO hearts (n = 7, P < 0.05). Intracardiac EPO injection restores myocardial functions following MI, which may attribute to the improved early recruitment of c-Kit(+) and CD34(+) stem cells via the enhanced expression of chemoattractant SDF-1.
Figures












References
-
- Jelkmann W, Wagner K. Beneficial and ominous aspects of the pleiotropic action of erythropoietin. Ann Hematol. 2004;83:673–86. - PubMed
-
- Zwezdaryk KJ, Coffelt SB, Figueroa YG, Liu J, Phinney DG, LaMarca HL, Florez L, Morris CB, Hoyle GW, Scandurro AB. Erythropoietin, a hypoxia-regulated factor, elicits a pro-angiogenic program in human mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Hematol. 2007;35:640–52. - PubMed
-
- Tramontano AF, Muniyappa R, Black AD, Blendea MC, Cohen I, Deng L, Sowers JR, Cutaia MV, El-Sherif N. Erythropoietin protects cardiac myocytes from hypoxia-induced apoptosis through an Akt-depend-ent pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003;308:990–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

