Sequestration of E12/E47 and suppression of p27KIP1 play a role in Id2-induced proliferation and tumorigenesis
- PMID: 19451188
- PMCID: PMC2704286
- DOI: 10.1093/carcin/bgp115
Sequestration of E12/E47 and suppression of p27KIP1 play a role in Id2-induced proliferation and tumorigenesis
Abstract
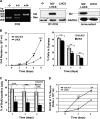
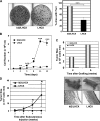
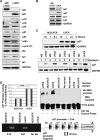
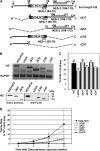
Id2 is a member of the helix-loop-helix (HLH) family of transcription regulators known to antagonize basic HLH transcription factors and proteins of the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor family and is implicated in the regulation of proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis and carcinogenesis. To investigate its proposed role in tumorigenesis, Id2 or deletion mutants were re-expressed in Id2(-/-) dermal fibroblasts. Ectopic expression of Id2 or mutants containing the central HLH domain increased S-phase cells, cell proliferation in low and normal serum and induced tumorigenesis when grafted or subcutaneously injected into athymic mice. Similar to their downregulation in human tumors, the expression of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors p27(KIP1) and p15(INK4b) was decreased by Id2; the former by downregulation of its promoter by the Id2 HLH domain-mediated sequestration of E12/E47. Re-expression of p27(KIP1) in Id2-overexpressing cells reverted the hyperproliferative and tumorigenic phenotype, implicating Id2 as an oncogene working through p27(KIP1). These results tie together the previously observed misregulation of Id2 with a novel mechanism for tumorigenesis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
FHL2 interacts with and acts as a functional repressor of Id2 in human neuroblastoma cells.Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 Jul;37(12):3996-4009. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp332. Epub 2009 May 5. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009. PMID: 19417068 Free PMC article.
-
E Proteins and Id2 converge on p57Kip2 to regulate cell cycle in neural cells.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Jun;26(11):4351-61. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01743-05. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16705184 Free PMC article.
-
Id2 promotes the invasive growth of MCF-7 and SKOV-3 cells by a novel mechanism independent of dimerization to basic helix-loop-helix factors.BMC Cancer. 2009 Mar 4;9:75. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-9-75. BMC Cancer. 2009. PMID: 19257909 Free PMC article.
-
Id2 promotes tumor cell migration and invasion through transcriptional repression of semaphorin 3F.Cancer Res. 2010 May 1;70(9):3823-32. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-3048. Epub 2010 Apr 13. Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20388805 Free PMC article.
-
ID2: A negative transcription factor regulating oligodendroglia differentiation.J Neurosci Res. 2012 May;90(5):925-32. doi: 10.1002/jnr.22826. Epub 2012 Jan 18. J Neurosci Res. 2012. PMID: 22253220 Review.
Cited by
-
Increased Expression of NPM1 Suppresses p27Kip1 Function in Cancer Cells.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Oct 8;12(10):2886. doi: 10.3390/cancers12102886. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33050036 Free PMC article.
-
Id2a functions to limit Notch pathway activity and thereby influence the transition from proliferation to differentiation of retinoblasts during zebrafish retinogenesis.Dev Biol. 2012 Nov 15;371(2):280-92. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2012.08.032. Epub 2012 Sep 8. Dev Biol. 2012. PMID: 22981606 Free PMC article.
-
RP58 controls neuron and astrocyte differentiation by downregulating the expression of Id1-4 genes in the developing cortex.EMBO J. 2012 Mar 7;31(5):1190-202. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2011.486. Epub 2012 Jan 10. EMBO J. 2012. PMID: 22234186 Free PMC article.
-
Smad7 restricts melanoma invasion by restoring N-cadherin expression and establishing heterotypic cell-cell interactions in vivo.Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2010 Dec;23(6):795-808. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-148X.2010.00758.x. Epub 2010 Aug 25. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2010. PMID: 20738806 Free PMC article.
-
Id3 induces an Elk-1-caspase-8-dependent apoptotic pathway in squamous carcinoma cells.Cancer Med. 2015 Jun;4(6):914-24. doi: 10.1002/cam4.427. Epub 2015 Feb 18. Cancer Med. 2015. PMID: 25693514 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Murre C, et al. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell. 1989;56:777–783. - PubMed
-
- Murre C, et al. Interactions between heterologous helix-loop-helix proteins generate complexes that bind specifically to a common DNA sequence. Cell. 1989;58:537–544. - PubMed
-
- Murre C, et al. Structure and function of helix-loop-helix proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1994;1218:129–135. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

