iNKT cell development is orchestrated by different branches of TGF-beta signaling
- PMID: 19451264
- PMCID: PMC2715067
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20090127
iNKT cell development is orchestrated by different branches of TGF-beta signaling
Abstract
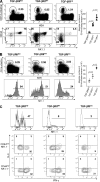
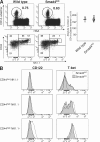
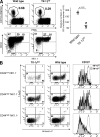
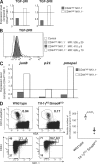
Invariant natural killer T (iNKT) cells constitute a distinct subset of T lymphocytes exhibiting important immune-regulatory functions. Although various steps of their differentiation have been well characterized, the factors controlling their development remain poorly documented. Here, we show that TGF-beta controls the differentiation program of iNKT cells. We demonstrate that TGF-beta signaling carefully and specifically orchestrates several steps of iNKT cell development. In vivo, this multifaceted role of TGF-beta involves the concerted action of different pathways of TGF-beta signaling. Whereas the Tif-1gamma branch controls lineage expansion, the Smad4 branch maintains the maturation stage that is initially repressed by a Tif-1gamma/Smad4-independent branch. Thus, these three different branches of TGF-beta signaling function in concert as complementary effectors, allowing TGF-beta to fine tune the iNKT cell differentiation program.
Figures



References
-
- Kronenberg M., Gapin L. 2002. The unconventional lifestyle of NKT cells.Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2:557–568 - PubMed
-
- Kronenberg M., Rudensky A. 2005. Regulation of immunity by self-reactive T cells.Nature. 435:598–604 - PubMed
-
- Godfrey D.I., MacDonald H.R., Kronenberg M., Smyth M.J., Van Kaer L. 2004. NKT cells: what's in a name? Nat. Rev. Immunol. 4:231–237 - PubMed
-
- Kronenberg M. 2005. Toward an understanding of NKT cell biology: progress and paradoxes.Annu. Rev. Immunol. 23:877–900 - PubMed
-
- Bendelac A., Savage P.B., Teyton L. 2007. The biology of NKT cells.Annu. Rev. Immunol. 25:297–336 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

