The main green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate counteracts semen-mediated enhancement of HIV infection
- PMID: 19451623
- PMCID: PMC2683882
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0811827106
The main green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate counteracts semen-mediated enhancement of HIV infection
Abstract
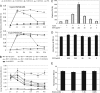
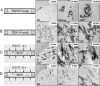
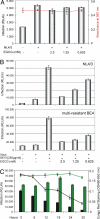
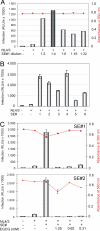
Peptide fragments, derived from prostatic acidic phosphatase, are secreted in large amounts into human semen and form amyloid fibrils. These fibrillar structures, termed semen-derived enhancer of virus infection (SEVI), capture HIV virions and direct them to target cells. Thus, SEVI appears to be an important infectivity factor of HIV during sexual transmission. Here, we are able to demonstrate that epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG), the major active constituent of green tea, targets SEVI for degradation. Furthermore, it is shown that EGCG inhibits SEVI activity and abrogates semen-mediated enhancement of HIV-1 infection in the absence of cellular toxicity. Therefore, EGCG appears to be a promising supplement to antiretroviral microbicides to reduce sexual transmission of HIV-1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- UNAIDS. [Accessed November 17, 2008];AIDS epidemic update. 2007 Available at http://data.unaids.org/pub/EPISlides/2007/071118_epi_regional%20factshee....
-
- Shattock RJ, Moore JP. Inhibiting sexual transmission of HIV-1 infection. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2003;1:25–34. - PubMed
-
- Klasse PJ, Shattock R, Moore JP. Antiretroviral drug-based microbicides to prevent HIV-1 sexual transmission. Annu Rev Med. 2008;59:455–471. - PubMed
-
- Münch J, et al. Semen-derived amyloid fibrils drastically enhance HIV infection. Cell. 2007;131:1059–1071. - PubMed
-
- Rönnberg L, Vihko P, Sajanti E, Vihko R. Clomiphene citrate administration to normogonadotropic subfertile men: Blood hormone changes and activation of acid phosphatase in seminal fluid. Int J Androl. 1981;4:372–378. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

