SARS-coronavirus modulation of myocardial ACE2 expression and inflammation in patients with SARS
- PMID: 19453650
- PMCID: PMC7163766
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.2009.02153.x
SARS-coronavirus modulation of myocardial ACE2 expression and inflammation in patients with SARS
Abstract
Background: Angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), a monocarboxylase that degrades angiotensin II to angiotensin 1-7, is also the functional receptor for severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) coronavirus (SARS-CoV) and is highly expressed in the lungs and heart. Patients with SARS also suffered from cardiac disease including arrhythmias, sudden cardiac death, and systolic and diastolic dysfunction.
Materials and methods: We studied mice infected with the human strain of the SARS-CoV and encephalomyocarditis virus and examined ACE2 mRNA and protein expression. Autopsy heart samples from patients who succumbed to the SARS crisis in Toronto (Canada) were used to investigate the impact of SARS on myocardial structure, inflammation and ACE2 protein expression.
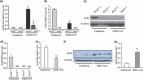
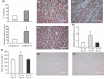
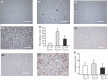
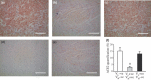
Results: Pulmonary infection with the human SARS-CoV in mice led to an ACE2-dependent myocardial infection with a marked decrease in ACE2 expression confirming a critical role of ACE2 in mediating SARS-CoV infection in the heart. The SARS-CoV viral RNA was detected in 35% (7/20) of autopsied human heart samples obtained from patients who succumbed to the SARS crisis during the Toronto SARS outbreak. Macrophage-specific staining showed a marked increase in macrophage infiltration with evidence of myocardial damage in patients who had SARS-CoV in their hearts. The presence of SARS-CoV in the heart was also associated with marked reductions in ACE2 protein expression.
Conclusions: Our data show that SARS-CoV can mediate myocardial inflammation and damage associated with down-regulation of myocardial ACE2 system, which may be responsible for the myocardial dysfunction and adverse cardiac outcomes in patients with SARS.
Figures
References
-
- Crackower MA, Sarao R, Oudit GY, Yagil C, Kozieradzki I, Scanga SE et al. Angiotensinconverting enzyme 2 is an essential regulator of heart function. Nature 2002;417:822–8. - PubMed
-
- Oudit GY, Crackower MA, Backx PH, Penninger JM. The role of ACE2 in cardiovascular physiology. Trends Cardiovasc Med 2003;13:93–101. - PubMed
-
- Oudit GY, Kassiri Z, Patel MP, Chappell M, Butany J, Backx PH et al. Angiotensin II‐mediated oxidative stress and inflammation mediate the age‐dependent cardiomyopathy in ACE2 null mice. Cardiovasc Res 2007;75:29–39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

