SGS: a structured treatment and teaching programme for older patients with diabetes mellitus--a prospective randomised controlled multi-centre trial
- PMID: 19454403
- PMCID: PMC2699189
- DOI: 10.1093/ageing/afp056
SGS: a structured treatment and teaching programme for older patients with diabetes mellitus--a prospective randomised controlled multi-centre trial
Abstract
Objectives: evaluation of the effectiveness of a new structured diabetes teaching and treatment programme (DTTP) with specific didactical approaches and topics for geriatric patients with diabetes mellitus.
Design: a prospective randomised controlled multi-centre trial.
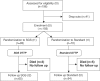
Setting and participants: a total of 155 geriatric patients were randomly admitted to either the new DTTP SGS (n = 83) or the standard DTTP (n = 72) for insulin-treated patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (HbA1c 8.0 +/- 1.4%, age 76.2 +/- 6.3 years).
Measurements: biometrical data, metabolic control, acute complications, diabetes knowledge, self-management.
Results: SGS participants showed improved levels of HbA1c 6 months after the DTTP, and less acute complications than the standard group (P<0.009). Both groups demonstrated a good capacity for diabetes self-management and improvement in diabetes knowledge after the DTTP (P<0.01).
Conclusion: the new SGS diabetes education programme, focusing on the learning capabilities and the particular needs of older persons, is effective in improving metabolic control and in maintaining auto-sufficiency in geriatric patients with diabetes mellitus.
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of a treatment and teaching refresher programme for the optimization of intensified insulin therapy in type 1 diabetes.Patient Educ Couns. 2013 Oct;93(1):108-13. doi: 10.1016/j.pec.2013.05.008. Epub 2013 Jun 6. Patient Educ Couns. 2013. PMID: 23747089
-
Substantial improvement in HbA1c following a treatment and teaching programme for people with type 2 diabetes on conventional insulin therapy in an in- and outpatient setting.Acta Diabetol. 2018 Feb;55(2):131-137. doi: 10.1007/s00592-017-1070-2. Epub 2017 Nov 17. Acta Diabetol. 2018. PMID: 29149381 Clinical Trial.
-
Structured treatment and teaching of patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus and impaired cognitive function--the DICOF trial.Diabet Med. 2004 Sep;21(9):999-1006. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.2004.01281.x. Diabet Med. 2004. PMID: 15317605
-
Evaluation of the SPECTRUM training programme for real-time continuous glucose monitoring: A real-world multicentre prospective study in 120 adults with type 1 diabetes.Diabet Med. 2021 Feb;38(2):e14467. doi: 10.1111/dme.14467. Epub 2020 Dec 10. Diabet Med. 2021. PMID: 33230860
-
The effectiveness of patient activation intervention on type 2 diabetes mellitus glycemic control and self-management behaviors: A systematic review of RCTs.Prim Care Diabetes. 2020 Feb;14(1):12-20. doi: 10.1016/j.pcd.2019.08.009. Epub 2019 Sep 20. Prim Care Diabetes. 2020. PMID: 31543458
Cited by
-
An evaluation of the effectiveness of a multi-modal intervention in frail and pre-frail older people with type 2 diabetes--the MID-Frail study: study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2014 Jan 24;15:34. doi: 10.1186/1745-6215-15-34. Trials. 2014. PMID: 24456998 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
[Diabetes mellitus].Z Gerontol Geriatr. 2017 Dec;50(8):676-679. doi: 10.1007/s00391-017-1315-2. Epub 2017 Oct 9. Z Gerontol Geriatr. 2017. PMID: 28993859 Review. German. No abstract available.
-
The effects of diabetes self-management programs on clinical and patient reported outcomes in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Clin Diabetes Healthc. 2024 Jun 17;5:1348104. doi: 10.3389/fcdhc.2024.1348104. eCollection 2024. Front Clin Diabetes Healthc. 2024. PMID: 38952998 Free PMC article.
-
Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Elderly Patients with Frailty and/or Sarcopenia.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Jul 16;19(14):8677. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19148677. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35886528 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification and prevalence of frailty in diabetes mellitus and association with clinical outcomes: a systematic review protocol.BMJ Open. 2020 Sep 1;10(9):e037476. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-037476. BMJ Open. 2020. PMID: 32873673 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Braun A, Müller UA, Müller R, et al. Structured treatment and teaching of patients with type-2 diabetes mellitus and impaired cognitive function—the DICOF trial. Diabet Med. 2004;21:999–1006. - PubMed
-
- Alberti G European policy Group 1998–1999 International Diabetes Federation European Region. A desktop guide to type 2 diabetes mellitus. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 1999;107:390–420. - PubMed
-
- Hader C, Beischer W, Braun A, et al. Diagnosis, treatment and follow-up of diabetes mellitus in elderly. Eur J Ger. 2006;8:1–57.
-
- Durso SC. Using clinical guidelines designed for older adults with diabetes mellitus and complex health status. JAMA. 2006;16:1935–40. - PubMed
-
- Berger M, Bott U, Grüßer M, et al. Cologne, Germany: Deutscher Ärzteverlag; 1990. Behandlungs- und Schulungsprogramm für Typ-II-Diabetiker, die Insulin spritzen.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical