Between celiac disease and irritable bowel syndrome: the "no man's land" of gluten sensitivity
- PMID: 19455131
- PMCID: PMC3480312
- DOI: 10.1038/ajg.2009.188
Between celiac disease and irritable bowel syndrome: the "no man's land" of gluten sensitivity
Abstract
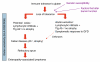
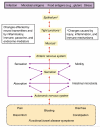
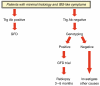
The repertoire of gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms is finite; however, the etiologies and mechanisms underlying symptom generation and perception are diverse and, in many cases, unknown. This review examines the clinical and experimental evidence exploring the putative relationship between gluten sensitivity (GS) and the generation of GI symptoms. It explores the hypothesis that, in a proportion of patients, GS causes functional bowel disorder (FBD)-like symptoms. We propose a model for investigating and understanding the induction of GI symptoms and dysfunction by gluten in FBD and organic disease. We hypothesize that, even in the absence of fully developed celiac disease, gluten can induce symptoms similar to FBD. We discuss the hypothesis that GS and post-infectious irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) provide two triggers that can explain at least part of the spectrum that constitutes IBS, further advancing an understanding of the role of mucosal responses to luminal factors in FBDs. We propose that the animal model of GS in human leukocyte antigen (HLA)- DQ8 mice allows investigation of mucosal pathophysiological changes that occur before the onset of full-blown inflammation in a GS host. A better understanding of how gluten can cause symptoms in sensitive individuals will illuminate the interaction between host genotype, diet, and intestinal microbiota in generating one of the most common GI conditions.
Figures

Comment in
-
Is gluten sensitivity a "No Man's Land" or a "Fertile Crescent" for research?Am J Gastroenterol. 2010 Jan;105(1):222-3; author reply 223-4. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2009.565. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010. PMID: 20054311 No abstract available.
References
-
- Fasano A, Berti I, Gerarduzzi T, et al. Prevalence of celiac disease in at-risk and not-at-risk groups in the United States: a large multicenter study. Arch Intern Med. 2003;163:286–92. - PubMed
-
- Cranney A, Zarkadas M, Graham ID, et al. The Canadian Celiac Health Survey. Dig Dis Sci. 2007;52:1087–95. - PubMed
-
- Catassi C, Ratsch JM, Fabiani E, et al. Coeliac disease in the year: exploring the iceberg. Lancet. 2000;343:200–3. C.G.D.S. - PubMed
-
- Csizmadia CG, Mearin ML, von Blomberg BME, et al. An iceberg of child-hood coeliac disease in the Netherlands. Lancet. 1999;353:813–4. - PubMed
-
- Weile I, Grodzinsky E, Skogh T, et al. High prevalence rates of adult silent celiac disease, as seen in Sweden, must be expected in Denmark. APMIS. 2001;109:745–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

