Data mining for gene networks relevant to poor prognosis in lung cancer via backward-chaining rule induction
- PMID: 19455237
- PMCID: PMC2312096
Data mining for gene networks relevant to poor prognosis in lung cancer via backward-chaining rule induction
Abstract
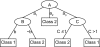
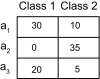
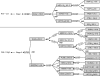
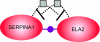
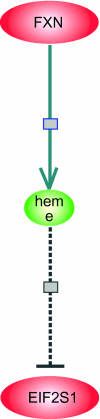
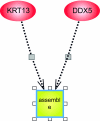
We use Backward Chaining Rule Induction (BCRI), a novel data mining method for hypothesizing causative mechanisms, to mine lung cancer gene expression array data for mechanisms that could impact survival. Initially, a supervised learning system is used to generate a prediction model in the form of "IF <conditions> THEN <outcome>" style rules. Next, each antecedent (i.e. an IF condition) of a previously discovered rule becomes the outcome class for subsequent application of supervised rule induction. This step is repeated until a termination condition is satisfied. "Chains" of rules are created by working backward from an initial condition (e.g. survival status). Through this iterative process of "backward chaining," BCRI searches for rules that describe plausible gene interactions for subsequent validation. Thus, BCRI is a semi-supervised approach that constrains the search through the vast space of plausible causal mechanisms by using a top-level outcome to kick-start the process. We demonstrate the general BCRI task sequence, how to implement it, the validation process, and how BCRI-rules discovered from lung cancer microarray data can be combined with prior knowledge to generate hypotheses about functional genomics.
Keywords: C4.5; class discovery; data analysis; decision trees; microarray; molecular mechanisms; non-small cell lung cancer; semi-supervised methods; systems biology.
Figures
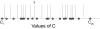
Similar articles
-
LEMRG: Decision Rule Generation Algorithm for Mining MicroRNA Expression Data.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;1028:105-137. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-6041-0_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 29058219 Review.
-
Semi-supervised incremental learning with few examples for discovering medical association rules.BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2022 Jan 24;22(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s12911-022-01755-3. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2022. PMID: 35073885 Free PMC article.
-
High confidence rule mining for microarray analysis.IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform. 2007 Oct-Dec;4(4):611-623. doi: 10.1109/tcbb.2007.1050. IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform. 2007. PMID: 17975272
-
Expert systems in histopathology. II. Knowledge representation and rule-based systems.Anal Quant Cytol Histol. 1989 Jun;11(3):147-53. Anal Quant Cytol Histol. 1989. PMID: 2663006 Review.
-
Graph- and rule-based learning algorithms: a comprehensive review of their applications for cancer type classification and prognosis using genomic data.Brief Bioinform. 2020 Mar 23;21(2):368-394. doi: 10.1093/bib/bby120. Brief Bioinform. 2020. PMID: 30649169 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical and molecular models of glioblastoma multiforme survival.Int J Data Min Bioinform. 2013;7(3):245-65. doi: 10.1504/ijdmb.2013.053310. Int J Data Min Bioinform. 2013. PMID: 23819258 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges of the information age: the impact of false discovery on pathway identification.BMC Res Notes. 2012 Nov 21;5:647. doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-5-647. BMC Res Notes. 2012. PMID: 23171633 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression meta-analysis supports existence of molecular apocrine breast cancer with a role for androgen receptor and implies interactions with ErbB family.BMC Med Genomics. 2009 Sep 11;2:59. doi: 10.1186/1755-8794-2-59. BMC Med Genomics. 2009. PMID: 19747394 Free PMC article.
-
A data mining based clinical decision support system for survival in lung cancer.Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 2021 Dec 30;26(6):839-848. doi: 10.5603/RPOR.a2021.0088. eCollection 2021. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 2021. PMID: 34992855 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anzick SL, Trent JM. Role of genomics in identifying new targets for cancer therapy. Oncology., (Huntingt) 2002;16(5 Suppl 4):7–13. - PubMed
-
- Beer D, Kardia S, Huang C, et al. Gene-expression profiles predict survival of patients with lung adenocarcinoma. Nature Medicine. 2002;8:816–824. - PubMed
-
- Bjorkhem-Bergman L, Jonsson-Videsater K, Paul C, et al. Mammalian thioredoxin reductase alters cytolytic activity of an antibacterial peptide. Peptides. 2004;25(11):1849–55. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
