Common genetic variation in the melatonin receptor 1B gene (MTNR1B) is associated with decreased early-phase insulin response
- PMID: 19455304
- PMCID: PMC2709880
- DOI: 10.1007/s00125-009-1392-x
Common genetic variation in the melatonin receptor 1B gene (MTNR1B) is associated with decreased early-phase insulin response
Abstract
Aims/hypothesis: We investigated whether variation in MTNR1B, which was recently identified as a common genetic determinant of fasting glucose levels in healthy, diabetes-free individuals, is associated with measures of beta cell function and whole-body insulin sensitivity.
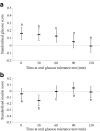
Methods: We studied 1,276 healthy individuals of European ancestry at 19 centres of the Relationship between Insulin Sensitivity and Cardiovascular disease (RISC) study. Whole-body insulin sensitivity was assessed by euglycaemic-hyperinsulinaemic clamp and indices of beta cell function were derived from a 75 g oral glucose tolerance test (including 30 min insulin response and glucose sensitivity). We studied rs10830963 in MTNR1B using additive genetic models, adjusting for age, sex and recruitment centre.
Results: The minor (G) allele of rs10830963 in MTNR1B (frequency 0.30 in HapMap Centre d'Etude du Polymorphisme [Utah residents with northern and western European ancestry] [CEU]; 0.29 in RISC participants) was associated with higher levels of fasting plasma glucose (standardised beta [95% CI] 0.17 [0.085, 0.25] per G allele, p = 5.8 x 10(-5)), consistent with recent observations. In addition, the G-allele was significantly associated with lower early insulin response (-0.19 [-0.28, -0.10], p = 1.7 x 10(-5)), as well as with decreased beta cell glucose sensitivity (-0.11 [-0.20, -0.027], p = 0.010). No associations were observed with clamp-assessed insulin sensitivity (p = 0.15) or different measures of body size (p > 0.7 for all).
Conclusions/interpretation: Genetic variation in MTNR1B is associated with defective early insulin response and decreased beta cell glucose sensitivity, which may contribute to the higher glucose levels of non-diabetic individuals carrying the minor G allele of rs10830963 in MTNR1B.
Figures

References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1086/509517', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1086/509517'}, {'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC1698701', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC1698701/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '17186458', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17186458/'}]}
- Weedon MN, Clark VJ, Qian Y et al (2006) A common haplotype of the glucokinase gene alters fasting glucose and birth weight: association in six studies and population-genetics analyses. Am J Hum Genet 79:991–1001 - PMC - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1126/science.1156849', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1156849'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '18451265', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18451265/'}]}
- Bouatia-Naji N, Rocheleau G, Van LL et al (2008) A polymorphism within the G6PC2 gene is associated with fasting plasma glucose levels. Science 320:1085–1088 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC2398737', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2398737/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '18521185', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18521185/'}]}
- Chen WM, Erdos MR, Jackson AU et al (2008) Variations in the G6PC2/ABCB11 genomic region are associated with fasting glucose levels. J Clin Invest 118:2620–2628 - PMC - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1126/science.1142358', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1142358'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '17463246', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17463246/'}]}
- Saxena R, Voight BF, Lyssenko V et al (2007) Genome-wide association analysis identifies loci for type 2 diabetes and triglyceride levels. Science 316:1331–1336 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.2337/db07-1807', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.2337/db07-1807'}, {'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC2494697', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2494697/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '18556336', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18556336/'}]}
- Vaxillaire M, Cavalcanti-Proenca C, Dechaume A et al (2008) The common P446L polymorphism in GCKR inversely modulates fasting glucose and triglyceride levels and reduces type 2 diabetes risk in the DESIR prospective general French population. Diabetes 57:2253–2257 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

