Fatty acid oxidation and meiotic resumption in mouse oocytes
- PMID: 19455666
- PMCID: PMC3995453
- DOI: 10.1002/mrd.21047
Fatty acid oxidation and meiotic resumption in mouse oocytes
Abstract
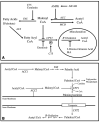
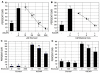
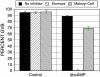
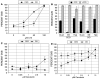
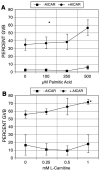
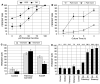
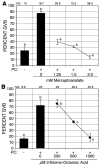
We have examined the potential role of fatty acid oxidation (FAO) in AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)-induced meiotic maturation. Etomoxir and malonyl CoA, two inhibitors of carnitine palmitoyl transferase-1 (CPT1), and thus FAO, blocked meiotic induction in dbcAMP-arrested cumulus cell-enclosed oocytes (CEO) and denuded oocytes (DO) by the AMPK activator, AICAR. C75, an activator of CPT1 and FAO, stimulated meiotic resumption in CEO and DO. This effect was insensitive to the AMPK inhibitor, compound C, indicating an action downstream of AMPK. Palmitic acid or carnitine also promoted meiotic resumption in DO in the presence of AICAR. Since C75 also suppresses the activity of fatty acid synthase (FAS), we tested another FAS inhibitor, cerulenin. Cerulenin stimulated maturation in arrested oocytes, but to a lesser extent, exhibited significantly slower kinetics and was effective in CEO but not DO. Moreover, etomoxir completely blocked C75-induced maturation but was ineffective in cerulenin-treated oocytes, suggesting that the meiosis-inducing action of C75 is through activation of FAO within the oocyte, while that of cerulenin is independent of FAO and acts within the cumulus cells. Finally, we determined that long chain, but not short chain, fatty acyl carnitine derivatives were stimulatory to oocyte maturation. Palmitoyl carnitine stimulated maturation in both CEO and DO, with rapid kinetics in DO; this effect was blocked by mercaptoacetate, a downstream inhibitor of FAO. These results indicate that activation of AMPK stimulates meiotic resumption in mouse oocytes by eliminating a block to FAO.
Figures

References
-
- Berger PS, Wood PA. Disrupted blastocoele formation reveals a critical developmental role for long-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase. Mol Gen Metab. 2004;82:266–272. - PubMed
-
- Carling D, Clarke PR, Zammit VA, Hardie DG. Purification and characterization of the AMP-activated protein kinase: copurification of acetyl-CoA carboxylase and 3-hydroxy-3-methyglutaryl-CoA reductase kinase activities. Eur J Biochem. 1989;186:129–136. - PubMed
-
- Carling D, Fryer L, Woods A, Daniel T, Jarvie S, Whitrow H. Bypassing the glucose/fatty acid cycle: AMP-activated protein kinase. Biochem Soc Trans. 2003;31:1157–1160. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

