A multi-target antisense approach against PDE4 and PDE7 reduces smoke-induced lung inflammation in mice
- PMID: 19457265
- PMCID: PMC2696437
- DOI: 10.1186/1465-9921-10-39
A multi-target antisense approach against PDE4 and PDE7 reduces smoke-induced lung inflammation in mice
Abstract
Background: Recent development in the field of COPD has focused on strategies aimed at reducing the underlying inflammation through selective inhibition of the phosphodiesterase type IV (PDE4) isoform. Although the anti-inflammatory and bronchodilator activity of selective PDE4 inhibitors has been well documented, their low therapeutic ratio and dose-dependent systemic side effects have limited their clinical utility. This study examined the effect of 2'-deoxy-2'-Fluoro-beta-D-Arabinonucleic Acid (FANA)-containing antisense oligonucleotides (AON) targeting the mRNA for the PDE4B/4D and 7A subtypes on lung inflammatory markers, both in vitro and in vivo.
Methods: Normal human bronchial epithelial (NHBE) cells were transfected with FANA AON against PDE4B/4D and 7A alone or in combination. mRNA levels for target PDE subtypes, as well as secretion of pro-inflammatory chemokines were then measured following cell stimulation. Mice were treated with combined PDE4B/4D and 7A AON via endo-tracheal delivery, or with roflumilast via oral delivery, and exposed to cigarette smoke for one week. Target mRNA inhibition, as well as influx of inflammatory cells and mediators were measured in lung lavages. A two-week smoke exposure protocol was also used to test the longer term potency of PDE4B/4D and 7A AONs.
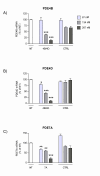
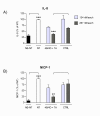
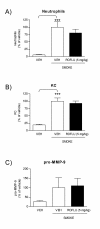
Results: In NHBE cells, PDE4B/4D and 7A AONs dose-dependently and specifically inhibited expression of their respective target mRNA. When used in combination, PDE4B/4D and 7A AONs significantly abrogated the cytokine-induced secretion of IL-8 and MCP-1 to near baseline levels. In mice treated with combined PDE4B/4D and 7A AONs and exposed to cigarette smoke, significant protection against the smoke-induced recruitment of neutrophils and production of KC and pro-MMP-9 was obtained, which was correlated with inhibition of target mRNA in cells from lung lavages. In this model, PDE AONs exerted more potent and broader anti-inflammatory effects against smoke-induced lung inflammation than roflumilast. Moreover, the protective effect of PDE4B/4D and 7A AON was maintained when a once-weekly treatment schedule was used.
Conclusion: These results indicate that inhaled AON against PDE4B/4D and 7A have unique effects on biomarkers that are believed to be important in the pathophysiology of COPD, which supports further development as a potential therapy in this disease.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The unrecognized effects of phosphodiesterase 4 on epithelial cells in pulmonary inflammation.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 24;10(4):e0121725. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0121725. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25909327 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of PDE4/PDE4B improves renal function and ameliorates inflammation in cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2020 Mar 1;318(3):F576-F588. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00477.2019. Epub 2020 Jan 21. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31961716
-
Roflumilast partially reverses smoke-induced mucociliary dysfunction.Respir Res. 2015 Oct 31;16:135. doi: 10.1186/s12931-015-0294-3. Respir Res. 2015. PMID: 26521141 Free PMC article.
-
The preclinical pharmacology of roflumilast--a selective, oral phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor in development for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2010 Aug;23(4):235-56. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2010.03.011. Epub 2010 Apr 7. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2010. PMID: 20381629 Review.
-
Phosphodiesterase inhibitors in airways disease.Eur J Pharmacol. 2006 Mar 8;533(1-3):110-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2005.12.059. Epub 2006 Feb 2. Eur J Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16458289 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibitory effects of Stemona tuberosa on lung inflammation in a subacute cigarette smoke-induced mouse model.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014 Dec 20;14:513. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-14-513. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014. PMID: 25528348 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and properties of 2'-deoxy-2',4'-difluoroarabinose-modified nucleic acids.J Org Chem. 2015 Mar 20;80(6):3083-91. doi: 10.1021/jo502948t. Epub 2015 Mar 5. J Org Chem. 2015. PMID: 25723361 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Phosphodiesterase 7 (PDE7) in T Cell Activity. Effects of Selective PDE7 Inhibitors and Dual PDE4/7 Inhibitors on T Cell Functions.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 25;21(17):6118. doi: 10.3390/ijms21176118. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32854348 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effects of BRL-50481 on ovalbumin-induced asthmatic lung inflammation exacerbated by co-exposure to Asian sand dust in the murine model.Arch Pharm Res. 2022 Jan;45(1):51-62. doi: 10.1007/s12272-021-01367-x. Epub 2022 Jan 4. Arch Pharm Res. 2022. PMID: 34984603 Free PMC article.
-
5'-O-Methylphosphonate nucleic acids--new modified DNAs that increase the Escherichia coli RNase H cleavage rate of hybrid duplexes.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Apr;42(8):5378-89. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku125. Epub 2014 Feb 12. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24523351 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

