Influence of nucleotide identity on ribose 2'-hydroxyl reactivity in RNA
- PMID: 19458034
- PMCID: PMC2704086
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.1536209
Influence of nucleotide identity on ribose 2'-hydroxyl reactivity in RNA
Abstract
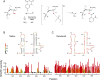
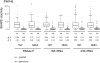
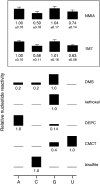
Hydroxyl-selective electrophiles, including N-methylisatoic anhydride (NMIA) and 1-methyl-7-nitroisatoic anhydride (1M7), are broadly useful for RNA structure analysis because they react preferentially with the ribose 2'-OH group at conformationally unconstrained or flexible nucleotides. Each nucleotide in an RNA has the potential to form an adduct with these reagents to yield a comprehensive, nucleotide-resolution, view of RNA structure. However, it is possible that factors other than local structure modulate reactivity. To evaluate the influence of base identity on the intrinsic reactivity of each nucleotide, we analyze NMIA and 1M7 reactivity using four distinct RNAs, under both native and denaturing conditions. We show that guanosine and adenosine residues have identical intrinsic 2'-hydroxyl reactivities at pH 8.0 and are 1.4 and 1.7 times more reactive than uridine and cytidine, respectively. These subtle, but statistically significant, differences do not impact the ability of selective 2'-hydroxyl acylation analyzed by primer extension-based (SHAPE) methods to establish an RNA secondary structure or monitor RNA folding in solution because base-specific influences are much smaller than the reactivity differences between paired and unpaired nucleotides.
Figures


References
-
- Acharya S, Foldesi A, Chattopadhyaya J. The pKa of the internucleotidic 2′-hydroxyl group in diribonucleoside (3′ →5′) monophosphates. J Org Chem. 2003;68:1906–1910. - PubMed
-
- Badorrek CS, Weeks KM. Architecture of a γ retroviral genomic RNA dimer. Biochemistry. 2006;45:12664–12672. - PubMed
-
- Cannone JJ, Subramanian S, Schnare MN, Collett JR, D'Souza LM, Du Y, Feng B, Lin N, Madabusi LV, Muller KM, et al. The Comparative RNA Web (CRW) site: An online database of comparative sequence and structure information for ribosomal, intron, and other RNAs. BMC Bioinformatics. 2002;3:2. - PMC - PubMed
-
- David L, Lambert D, Gendron P, Major F. Leadzyme. Methods Enzymol. 2001;341:518–540. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
