Peptidyl-prolyl isomerase Pin1 markedly enhances the oncogenic activity of the rel proteins in the nuclear factor-kappaB family
- PMID: 19458071
- PMCID: PMC2741415
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-4117
Peptidyl-prolyl isomerase Pin1 markedly enhances the oncogenic activity of the rel proteins in the nuclear factor-kappaB family
Abstract
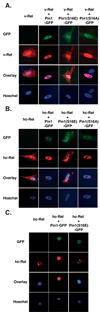
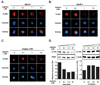
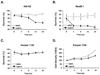
The peptidyl-prolyl isomerase Pin1 is frequently up-regulated in human cancers in which Rel/nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) is constitutively activated, but its role in these cancers remains to be determined, and evidence is still lacking to show that Pin1 contributes to cell transformation by Rel/NF-kappaB. Rel/NF-kappaB transcriptional and oncogenic activities are modulated by several posttranslational modifications and coregulatory proteins, and previous studies showed that cytokine treatment induces binding of Pin1 to the RelA subunit of NF-kappaB, thereby enhancing RelA nuclear localization and stability. Here we show that Pin1 associates with the Rel subunits of NF-kappaB that are implicated in leukemia/lymphomagenesis and modulates their transcriptional and oncogenic activities. Pin1 markedly enhanced transformation of primary lymphocytes by the human c-Rel protein and also increased cell transformation by the potent viral Rel/NF-kappaB oncoprotein v-Rel, in contrast to a Pin1 mutant in the WW domain involved in interaction with NF-kappaB. Pin1 promoted nuclear accumulation of Rel proteins in the absence of activating stimuli. Importantly, inhibition of Pin1 function with the pharmacologic inhibitor juglone or with Pin1-specific shRNA led to cytoplasmic relocalization of endogenous c-Rel in human lymphoma-derived cell lines, markedly interfered with lymphoma cell proliferation, and suppressed endogenous Rel/NF-kappaB-dependent gene expression. Together, these results show that Pin1 is an important regulator of Rel/NF-kappaB transforming activity and suggest that Pin1 may be a potential therapeutic target in Rel/NF-kappaB-dependent leukemia/lymphomas.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
The prolyl isomerase Pin1 enhances HER-2 expression and cellular transformation via its interaction with mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase 1.Mol Cancer Ther. 2010 Mar;9(3):606-16. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-09-0560. Epub 2010 Feb 23. Mol Cancer Ther. 2010. PMID: 20179161
-
The peptidyl-prolyl isomerase, Pin1, facilitates NF-kappaB binding in hepatocytes and protects against hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury.J Hepatol. 2009 Aug;51(2):296-306. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2009.04.016. Epub 2009 May 24. J Hepatol. 2009. PMID: 19515451 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of NF-kappaB signaling by Pin1-dependent prolyl isomerization and ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis of p65/RelA.Mol Cell. 2003 Dec;12(6):1413-26. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(03)00490-8. Mol Cell. 2003. PMID: 14690596
-
[Pin1: a multi-talented peptidyl prolyl cis-trans isomerase and a promising therapeutic target for human cancers].Med Sci (Paris). 2014 Aug-Sep;30(8-9):772-8. doi: 10.1051/medsci/20143008015. Epub 2014 Sep 1. Med Sci (Paris). 2014. PMID: 25174754 Review. French.
-
The peptidyl-prolyl isomerase Pin1.Prog Cell Cycle Res. 2003;5:477-87. Prog Cell Cycle Res. 2003. PMID: 14593743 Review.
Cited by
-
c-Rel gain in B cells drives germinal center reactions and autoantibody production.J Clin Invest. 2020 Jun 1;130(6):3270-3286. doi: 10.1172/JCI124382. J Clin Invest. 2020. PMID: 32191641 Free PMC article.
-
Prolyl isomerase Pin1 in cancer.Cell Res. 2014 Sep;24(9):1033-49. doi: 10.1038/cr.2014.109. Epub 2014 Aug 15. Cell Res. 2014. PMID: 25124924 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of peptidyl-prolyl isomerase Pin1 in disease pathogenesis.Theranostics. 2021 Jan 19;11(7):3348-3358. doi: 10.7150/thno.45889. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33537091 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pin1-catalyzed conformational regulation after phosphorylation: A distinct checkpoint in cell signaling and drug discovery.Sci Signal. 2024 Jun 18;17(841):eadi8743. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.adi8743. Epub 2024 Jun 18. Sci Signal. 2024. PMID: 38889227 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pin1 Inhibitor Juglone Exerts Anti-Oncogenic Effects on LNCaP and DU145 Cells despite the Patterns of Gene Regulation by Pin1 Differing between These Cell Lines.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 3;10(6):e0127467. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0127467. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26039047 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bonizzi G, Karin M. The two NF-kappaB activation pathways and their role in innate and adaptive immunity. Trends Immunol. 2004;25:280–288. - PubMed
-
- Campbell KJ, Rocha S, Perkins ND. Active repression of antiapoptotic gene expression by RelA(p65) NF-kappa B. Mol Cell. 2004;13:853–865. - PubMed
-
- Majid SM, Liss AS, You M, Bose HR. The suppression of SH3BGRL is important for v-Rel-mediated transformation. Oncogene. 2006;25:756–768. - PubMed
-
- Dutta J, Fan Y, Gupta N, Fan G, Gelinas C. Current insights into the regulation of programmed cell death by NF-κB. Oncogene. 2006;25:6800–6816. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

