MEME SUITE: tools for motif discovery and searching
- PMID: 19458158
- PMCID: PMC2703892
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkp335
MEME SUITE: tools for motif discovery and searching
Abstract
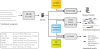
The MEME Suite web server provides a unified portal for online discovery and analysis of sequence motifs representing features such as DNA binding sites and protein interaction domains. The popular MEME motif discovery algorithm is now complemented by the GLAM2 algorithm which allows discovery of motifs containing gaps. Three sequence scanning algorithms--MAST, FIMO and GLAM2SCAN--allow scanning numerous DNA and protein sequence databases for motifs discovered by MEME and GLAM2. Transcription factor motifs (including those discovered using MEME) can be compared with motifs in many popular motif databases using the motif database scanning algorithm TOMTOM. Transcription factor motifs can be further analyzed for putative function by association with Gene Ontology (GO) terms using the motif-GO term association tool GOMO. MEME output now contains sequence LOGOS for each discovered motif, as well as buttons to allow motifs to be conveniently submitted to the sequence and motif database scanning algorithms (MAST, FIMO and TOMTOM), or to GOMO, for further analysis. GLAM2 output similarly contains buttons for further analysis using GLAM2SCAN and for rerunning GLAM2 with different parameters. All of the motif-based tools are now implemented as web services via Opal. Source code, binaries and a web server are freely available for noncommercial use at http://meme.nbcr.net.
Figures






References
-
- Bailey TL, Elkan CP. Fitting a mixture model by expectation-maximization to discover motifs in biopolymers. In: Altman R, Brutlag D, Karp P, Lathrop R, Searls D, editors. Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Intelligent Systems for Molecular Biology. Menlo Park, CA: AAAI Press; 1994. pp. 28–36. - PubMed
-
- Bailey TL, Gribskov M. Combining evidence using p-values: application to sequence homology searches. Bioinformatics. 1998;14:48–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

