Regulation of cell polarity through phosphorylation of Bni4 by Pho85 G1 cyclin-dependent kinases in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 19458192
- PMCID: PMC2710841
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e08-12-1255
Regulation of cell polarity through phosphorylation of Bni4 by Pho85 G1 cyclin-dependent kinases in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
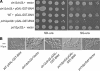
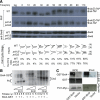
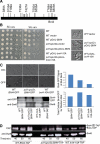
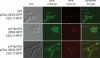
In the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, the G1-specific cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks) Cln1,2-Cdc28 and Pcl1,2-Pho85 are essential for ensuring that DNA replication and cell division are properly linked to cell polarity and bud morphogenesis. However, the redundancy of Cdks and cyclins means that identification of relevant Cdk substrates remains a significant challenge. We used array-based genetic screens (synthetic genetic array or SGA analysis) to dissect redundant pathways associated with G1 cyclins and identified Bni4 as a substrate of the Pcl1- and Pcl2-Pho85 kinases. BNI4 encodes an adaptor protein that targets several proteins to the bud neck. Deletion of BNI4 results in severe growth defects in the absence of the Cdc28 cyclins Cln1 and Cln2, and overexpression of BNI4 is toxic in yeast cells lacking the Pho85 cyclins Pcl1 and Pcl2. Phosphorylation of Bni4 by Pcl-Pho85 is necessary for its localization to the bud neck, and the bud neck structure can be disrupted by overexpressing BNI4 in pcl1Deltapcl2Delta mutant cells. Our data suggest that misregulated Bni4 may bind in an uncontrolled manner to an essential component that resides at the bud neck, causing catastrophic morphogenesis defects.
Figures



Comment in
- Mol Biol Cell. 20:3169.
Similar articles
-
Interaction of yeast Rvs167 and Pho85 cyclin-dependent kinase complexes may link the cell cycle to the actin cytoskeleton.Curr Biol. 1998 Dec 3;8(24):1310-21. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(07)00561-1. Curr Biol. 1998. PMID: 9843683
-
A family of cyclin-like proteins that interact with the Pho85 cyclin-dependent kinase.Mol Cell Biol. 1997 Mar;17(3):1212-23. doi: 10.1128/MCB.17.3.1212. Mol Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9032248 Free PMC article.
-
Late-G1 cyclin-CDK activity is essential for control of cell morphogenesis in budding yeast.Nat Cell Biol. 2004 Jan;6(1):59-66. doi: 10.1038/ncb1078. Epub 2003 Dec 14. Nat Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 14688790
-
Pho85, a multifunctional cyclin-dependent protein kinase in budding yeast.Mol Microbiol. 2007 Oct;66(2):303-14. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2007.05914.x. Epub 2007 Sep 10. Mol Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17850263 Review.
-
Functions of Pho85 cyclin-dependent kinases in budding yeast.Prog Cell Cycle Res. 2000;4:97-106. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-4253-7_9. Prog Cell Cycle Res. 2000. PMID: 10740818 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the yeast acetylome using functional genomics.Cell. 2012 May 11;149(4):936-48. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.02.064. Cell. 2012. PMID: 22579291 Free PMC article.
-
An overview of Cdk1-controlled targets and processes.Cell Div. 2010 May 13;5:11. doi: 10.1186/1747-1028-5-11. Cell Div. 2010. PMID: 20465793 Free PMC article.
-
A chemical-genetic screen to unravel the genetic network of CDC28/CDK1 links ubiquitin and Rad6-Bre1 to cell cycle progression.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Nov 15;108(46):18748-53. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1115885108. Epub 2011 Oct 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 22042866 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in Bni4 localization induced by cell stress in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.J Cell Sci. 2010 Apr 1;123(Pt 7):1050-9. doi: 10.1242/jcs.066258. Epub 2010 Mar 2. J Cell Sci. 2010. PMID: 20197406 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of small GTPase activity by G1 cyclins.Small GTPases. 2019 Jan;10(1):47-53. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2016.1268665. Epub 2017 Jan 27. Small GTPases. 2019. PMID: 28129038 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barral Y., Mermall V., Mooseker M. S., Snyder M. Compartmentalization of the cell cortex by septins is required for maintenance of cell polarity in yeast. Mol. Cell. 2000;5:841–851. - PubMed
-
- Boone C., Bussey H., Andrews B. J. Exploring genetic interactions and networks with yeast. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2007;8:437–449. - PubMed
-
- Brachmann C. B., Davies A., Cost G. J., Caputo E., Li J., Hieter P., Boeke J. D. Designer deletion strains derived from Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C: a useful set of strains and plasmids for PCR-mediated gene disruption and other applications. Yeast. 1998;14:115–132. - PubMed
-
- Cid V. J., Adamikova L., Sanchez M., Molina M., Nombela C. Cell cycle control of septin ring dynamics in the budding yeast. Microbiology. 2001;147:1437–1450. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

