Filamin A-beta1 integrin complex tunes epithelial cell response to matrix tension
- PMID: 19458194
- PMCID: PMC2710838
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e08-12-1186
Filamin A-beta1 integrin complex tunes epithelial cell response to matrix tension
Abstract
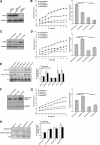
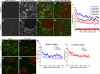
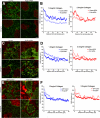
The physical properties of the extracellular matrix (ECM) regulate the behavior of several cell types; yet, mechanisms by which cells recognize and respond to changes in these properties are not clear. For example, breast epithelial cells undergo ductal morphogenesis only when cultured in a compliant collagen matrix, but not when the tension of the matrix is increased by loading collagen gels or by increasing collagen density. We report that the actin-binding protein filamin A (FLNa) is necessary for cells to contract collagen gels, and pull on collagen fibrils, which leads to collagen remodeling and morphogenesis in compliant, low-density gels. In stiffer, high-density gels, cells are not able to contract and remodel the matrix, and morphogenesis does not occur. However, increased FLNa-beta1 integrin interactions rescue gel contraction and remodeling in high-density gels, resulting in branching morphogenesis. These results suggest morphogenesis can be "tuned" by the balance between cell-generated contractility and opposing matrix stiffness. Our findings support a role for FLNa-beta1 integrin as a mechanosensitive complex that bidirectionally senses the tension of the matrix and, in turn, regulates cellular contractility and response to this matrix tension.
Figures



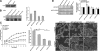


Comment in
- Mol Biol Cell. 20:3169.
Similar articles
-
Filamin A is required for vimentin-mediated cell adhesion and spreading.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2010 Feb;298(2):C221-36. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00323.2009. Epub 2009 Sep 23. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2010. PMID: 19776392 Free PMC article.
-
Filamin and filamin-binding proteins in integrin-regulation and adhesion. Focus on: "FilaminA is required for vimentin-mediated cell adhesion and spreading".Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2010 Feb;298(2):C206-8. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00505.2009. Epub 2009 Nov 18. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2010. PMID: 19923422 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Filamin A controls matrix metalloproteinase activity and regulates cell invasion in human fibrosarcoma cells.J Cell Sci. 2012 Aug 15;125(Pt 16):3858-69. doi: 10.1242/jcs.104018. Epub 2012 May 17. J Cell Sci. 2012. PMID: 22595522 Free PMC article.
-
Filling gaps in signaling to actin cytoskeletal remodeling.Dev Cell. 2003 Apr;4(4):444-5. doi: 10.1016/s1534-5807(03)00098-4. Dev Cell. 2003. PMID: 12689583 Review.
-
Filamin A mediates interactions between cytoskeletal proteins that control cell adhesion.FEBS Lett. 2011 Jan 3;585(1):18-22. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2010.11.033. Epub 2010 Nov 21. FEBS Lett. 2011. PMID: 21095189 Review.
Cited by
-
The Extracellular Matrix Stiffening: A Trigger of Prostate Cancer Progression and Castration Resistance?Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jun 11;14(12):2887. doi: 10.3390/cancers14122887. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35740556 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular matrix degradation and remodeling in development and disease.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2011 Dec 1;3(12):a005058. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a005058. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2011. PMID: 21917992 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of mechanical signaling in development and disease.J Cell Sci. 2011 Jan 1;124(Pt 1):9-18. doi: 10.1242/jcs.071001. J Cell Sci. 2011. PMID: 21172819 Free PMC article.
-
Filamins in mechanosensing and signaling.Annu Rev Biophys. 2012;41:227-46. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biophys-050511-102252. Epub 2012 Feb 23. Annu Rev Biophys. 2012. PMID: 22404683 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mammary gland ECM remodeling, stiffness, and mechanosignaling in normal development and tumor progression.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2011 Jan 1;3(1):a003228. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a003228. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2011. PMID: 20980442 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adelstein R. S., Eisenberg E. Regulation and kinetics of the actin-myosin-ATP interaction. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1980;49:921–956. - PubMed
-
- Bellanger J.-M., Astier C., Sarde C., Ohta Y., Stossel T. P., Debant A. The Rac1- and RhoG-specific GEF domain of Trio targets filamin to remodel cytoskeletal actin. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000;2:888–892. - PubMed
-
- Boyd N. F., Martin L. J., Stone J., Greenberg C., Minkin S., Yaffe M. J. Mammographic densities as a marker of human breast cancer risk and their use in chemoprevention. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2001;3:314–321. - PubMed
-
- Brown E., McKee T., diTomaso E., Pluen A., Seed B., Boucher Y., Jain R. K. Dynamic imaging of collagen and its modulation in tumors in vivo using second-harmonic generation. Nat. Med. 2003;9:796–800. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

