Membrane resonance in bursting pacemaker neurons of an oscillatory network is correlated with network frequency
- PMID: 19458214
- PMCID: PMC2716082
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0545-09.2009
Membrane resonance in bursting pacemaker neurons of an oscillatory network is correlated with network frequency
Abstract
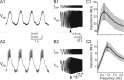
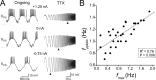
Network oscillations typically span a limited range of frequency. In pacemaker-driven networks, including many central pattern generators (CPGs), this frequency range is determined by the properties of bursting pacemaker neurons and their synaptic connections; thus, factors that affect the burst frequency of pacemaker neurons should play a role in determining the network frequency. We examine the role of membrane resonance of pacemaker neurons on the network frequency in the crab pyloric CPG. The pyloric oscillations (frequency of approximately 1 Hz) are generated by a group of pacemaker neurons: the anterior burster (AB) and the pyloric dilator (PD). We examine the impedance profiles of the AB and PD neurons in response to sinusoidal current injections with varying frequency and find that both neuron types exhibit membrane resonance, i.e., demonstrate maximal impedance at a given preferred frequency. The membrane resonance frequencies of the AB and PD neurons fall within the range of the pyloric network oscillation frequency. Experiments with pharmacological blockers and computational modeling show that both calcium currents I(Ca) and the hyperpolarization-activated inward current I(h) are important in producing the membrane resonance in these neurons. We then demonstrate that both the membrane resonance frequency of the PD neuron and its suprathreshold bursting frequency can be shifted in the same direction by either direct current injection or by using the dynamic-clamp technique to inject artificial conductances for I(h) or I(Ca). Together, these results suggest that membrane resonance of pacemaker neurons can be strongly correlated with the CPG oscillation frequency.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The membrane potential waveform of bursting pacemaker neurons is a predictor of their preferred frequency and the network cycle frequency.J Neurosci. 2010 Aug 11;30(32):10809-19. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1818-10.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20702710 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct synaptic dynamics of heterogeneous pacemaker neurons in an oscillatory network.J Neurophysiol. 2007 Mar;97(3):2239-53. doi: 10.1152/jn.01161.2006. Epub 2007 Jan 3. J Neurophysiol. 2007. PMID: 17202242 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term neuromodulatory regulation of a motor pattern-generating network: maintenance of synaptic efficacy and oscillatory properties.J Neurophysiol. 2002 Dec;88(6):2942-53. doi: 10.1152/jn.00482.2001. J Neurophysiol. 2002. PMID: 12466420
-
Oscillations and oscillatory behavior in small neural circuits.Biol Cybern. 2006 Dec;95(6):537-54. doi: 10.1007/s00422-006-0125-1. Epub 2006 Dec 7. Biol Cybern. 2006. PMID: 17151878 Review.
-
Novel modes of rhythmic burst firing at cognitively-relevant frequencies in thalamocortical neurons.Brain Res. 2008 Oct 15;1235:12-20. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2008.06.029. Epub 2008 Jun 19. Brain Res. 2008. PMID: 18602904 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Membrane potential resonance in non-oscillatory neurons interacts with synaptic connectivity to produce network oscillations.J Comput Neurosci. 2019 Apr;46(2):169-195. doi: 10.1007/s10827-019-00710-y. Epub 2019 Mar 20. J Comput Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30895410
-
Ih from synapses to networks: HCN channel functions and modulation in neurons.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2021 Nov;166:119-132. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2021.06.002. Epub 2021 Jun 25. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34181891 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multimodal Functional Analysis Platform: 4. Optogenetics-Induced Oscillatory Activation to Explore Neural Circuits.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1293:501-509. doi: 10.1007/978-981-15-8763-4_34. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 33398837
-
Distinct mechanisms underlie electrical coupling resonance and its interaction with membrane potential resonance.Front Syst Biol. 2023 Mar 8;3:1122433. doi: 10.3389/fsysb.2023.1122433. eCollection 2023. Front Syst Biol. 2023. PMID: 40809478 Free PMC article.
-
Measurement of the entrainment window of islets of Langerhans by microfluidic delivery of a chirped glucose waveform.Integr Biol (Camb). 2015 Sep;7(9):1061-7. doi: 10.1039/c5ib00156k. Epub 2015 Jul 27. Integr Biol (Camb). 2015. PMID: 26211670 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Art JJ, Crawford AC, Fettiplace R. Electrical resonance and membrane currents in turtle cochlear hair cells. Hear Res. 1986;22:31–36. - PubMed
-
- Bellingham MC. Driving respiration: the respiratory central pattern generator. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1998;25:847–856. - PubMed
-
- Brunel N, Hakim V, Richardson MJ. Firing-rate resonance in a generalized integrate-and-fire neuron with subthreshold resonance. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 2003;67 051916. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
