Central opioid inhibition of neuroendocrine stress responses in pregnancy in the rat is induced by the neurosteroid allopregnanolone
- PMID: 19458216
- PMCID: PMC6665894
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0708-09.2009
Central opioid inhibition of neuroendocrine stress responses in pregnancy in the rat is induced by the neurosteroid allopregnanolone
Abstract
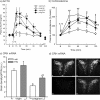
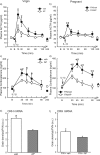
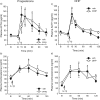
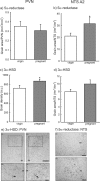
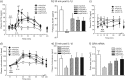
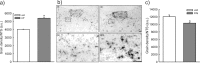
The hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis is the major neuroendocrine stress response system. Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) neurons in the parvocellular paraventricular nucleus (pPVN) play a key role in coordinating responses of this system to stressors. The cytokine interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta), mimicking infection, robustly activates these CRH neurons via a noradrenergic input arising from the nucleus tractus solitarii (NTS). In late pregnancy, HPA axis responses to stressors, including IL-1beta, are attenuated by a central opioid mechanism that auto-inhibits noradrenaline release in the PVN. Here we show that the neuroactive progesterone metabolite allopregnanolone induces these changes in HPA responsiveness to IL-1beta in pregnancy. In late pregnancy, inhibition of 5alpha-reductase (an allopregnanolone-synthesizing enzyme) with finasteride restored HPA axis responses (rapidly increased pPVN CRH mRNA expression, ACTH, and corticosterone secretion) to IL-1beta. Conversely, allopregnanolone reduced HPA responses in virgin rats. In late pregnancy, activity of the allopregnanolone-synthesizing enzymes (5alpha-reductase and 3alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase) was increased in the hypothalamus as was mRNA expression in the NTS and PVN. Naloxone, an opioid antagonist, restores HPA axis responses to IL-1beta in pregnancy but had no additional effect after finasteride, indicating a causal connection between allopregnanolone and the endogenous opioid mechanism. Indeed, allopregnanolone induced opioid inhibition over HPA responses to IL-1beta in virgin rats. Furthermore, in virgin rats, allopregnanolone treatment increased, whereas in pregnant rats finasteride decreased proenkephalin-A mRNA expression in the NTS. Thus, in pregnancy, allopregnanolone induces opioid inhibition over HPA axis responses to immune challenge. This novel opioid-mediated mechanism of allopregnanolone action may alter regulation of other brain systems in pregnancy.
Figures
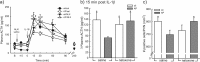
References
-
- Bailey TW, Appleyard SM, Jin YH, Andresen MC. Organization and properties of GABAergic neurons in solitary tract nucleus (NTS) J Neurophysiol. 2008;99:1712–1722. - PubMed
-
- Bali B, Kovács KJ. GABAergic control of neuropeptide gene expression in parvocellular neurons of the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus. Eur J Neurosci. 2003;18:1518–1526. - PubMed
-
- Beaulieu J, Champagne D, Drolet G. Enkephalin innervation of the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus: distribution of fibers and origins of input. J Chem Neuroanat. 1996;10:79–92. - PubMed
-
- Bertics SJ, Bertics PJ, Clarke JL, Karavolas HJ. Distribution and ovarian control of progestin-metabolizing enzymes in various rat hypothalamic regions. J Steroid Biochem. 1987;26:321–328. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
