Natural, metaphoric, and linguistic auditory direction signals have distinct influences on visual motion processing
- PMID: 19458220
- PMCID: PMC6665909
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5437-08.2009
Natural, metaphoric, and linguistic auditory direction signals have distinct influences on visual motion processing
Abstract
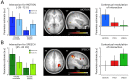
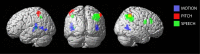
To interact with our dynamic environment, the brain merges motion information from auditory and visual senses. However, not only "natural" auditory MOTION, but also "metaphoric" de/ascending PITCH and SPEECH (e.g., "left/right"), influence the visual motion percept. Here, we systematically investigate whether these three classes of direction signals influence visual motion perception through shared or distinct neural mechanisms. In a visual-selective attention paradigm, subjects discriminated the direction of visual motion at several levels of reliability, with an irrelevant auditory stimulus being congruent, absent, or incongruent. Although the natural, metaphoric, and linguistic auditory signals were equally long and adjusted to induce a comparable directional bias on the motion percept, they influenced visual motion processing at different levels of the cortical hierarchy. A significant audiovisual interaction was revealed for MOTION in left human motion complex (hMT+/V5+) and for SPEECH in right intraparietal sulcus. In fact, the audiovisual interaction gradually decreased in left hMT+/V5+ for MOTION > PITCH > SPEECH and in right intraparietal sulcus for SPEECH > PITCH > MOTION. In conclusion, natural motion signals are integrated in audiovisual motion areas, whereas the influence of culturally learnt signals emerges primarily in higher-level convergence regions.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Sensory and striatal areas integrate auditory and visual signals into behavioral benefits during motion discrimination.J Neurosci. 2013 May 15;33(20):8841-9. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3020-12.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23678126 Free PMC article.
-
Physical and perceptual factors shape the neural mechanisms that integrate audiovisual signals in speech comprehension.J Neurosci. 2011 Aug 3;31(31):11338-50. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6510-10.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21813693 Free PMC article.
-
Speech comprehension aided by multiple modalities: behavioural and neural interactions.Neuropsychologia. 2012 Apr;50(5):762-76. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2012.01.010. Epub 2012 Jan 17. Neuropsychologia. 2012. PMID: 22266262 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial attention can modulate audiovisual integration at multiple cortical and subcortical sites.Eur J Neurosci. 2009 Mar;29(6):1247-57. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2009.06688.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19302160
-
The development of sensorimotor influences in the audiovisual speech domain: some critical questions.Front Psychol. 2014 Aug 6;5:812. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2014.00812. eCollection 2014. Front Psychol. 2014. PMID: 25147528 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Synesthetic Correspondence: An Overview.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1437:101-119. doi: 10.1007/978-981-99-7611-9_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 38270856 Review.
-
Effects of pitch and musical sounds on body-representations when moving with sound.Sci Rep. 2022 Feb 17;12(1):2676. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-06210-x. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35177677 Free PMC article.
-
The Influence of Auditory Cues on Bodily and Movement Perception.Front Psychol. 2020 Jan 17;10:3001. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.03001. eCollection 2019. Front Psychol. 2020. PMID: 32010030 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How many categories are there in crossmodal correspondences? A study based on exploratory factor analysis.PLoS One. 2023 Nov 14;18(11):e0294141. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0294141. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37963160 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of pitch-space correspondence on sound-induced visual motion perception.Exp Brain Res. 2013 Nov;231(1):117-26. doi: 10.1007/s00221-013-3674-2. Epub 2013 Sep 13. Exp Brain Res. 2013. PMID: 24030519
References
-
- Alais D, Burr D. No direction-specific bimodal facilitation for audiovisual motion detection. Brain Res Cogn Brain Res. 2004;19:185–194. - PubMed
-
- Bartels A, Zeki S, Logothetis NK. Natural vision reveals regional specialization to local motion and to contrast-invariant, global flow in the human brain. Cereb Cortex. 2008;18:705–717. - PubMed
-
- Baumann O, Greenlee MW. Neural correlates of coherent audiovisual motion perception. Cereb Cortex. 2007;17:1433–1443. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
