Reggies/flotillins regulate retinal axon regeneration in the zebrafish optic nerve and differentiation of hippocampal and N2a neurons
- PMID: 19458231
- PMCID: PMC6665911
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0870-09.2009
Reggies/flotillins regulate retinal axon regeneration in the zebrafish optic nerve and differentiation of hippocampal and N2a neurons
Abstract
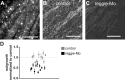
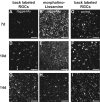
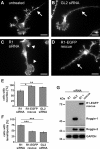
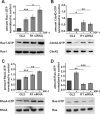
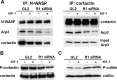
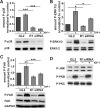
The reggies/flotillins--proteins upregulated during axon regeneration in retinal ganglion cells (RGCs)--are scaffolding proteins of microdomains and involved in neuronal differentiation. Here, we show that reggies regulate axon regeneration in zebrafish (ZF) after optic nerve section (ONS) in vivo as well as axon/neurite extension in hippocampal and N2a neurons in vitro through signal transduction molecules modulating actin dynamics. ZF reggie-1a, -2a, and -2b downregulation by reggie-specific morpholino (Mo) antisense oligonucleotides directly after ONS significantly reduced ZF RGC axon regeneration: RGC axons from reggie Mo retinas were markedly reduced. Moreover, the number of axon-regenerating RGCs, identified by insertion of A488-coupled dextran, decreased by 69% in retinas 7 d after Mo application. At 10 and 14 d, RGCs decreased by 53 and 33%, respectively, in correlation with the gradual inactivation of the Mos. siRNA-mediated knockdown of reggie-1 and -2 inhibited the differentiation and axon/neurite extension in hippocampal and N2a neurons. N2a cells had significantly shorter filopodia, more cells had lamellipodia and fewer neurites, defects which were rescued by a reggie-1 construct without siRNA-binding sites. Furthermore, reggie knockdown strongly perturbed the balanced activation of the Rho family GTPases Rac1, RhoA, and cdc42, influenced the phosphorylation of cortactin and cofilin, the formation of the N-WASP, cortactin and Arp3 complex, and affected p38, Ras, ERK1/2 (extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2), and focal adhesion kinase activation. Thus, as suggested by their prominent re-expression after lesion, the reggies represent neuron-intrinsic factors for axon outgrowth and regeneration, being crucial for the coordinated assembly of signaling complexes regulating cytoskeletal remodeling.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Reggies/flotillins regulate cytoskeletal remodeling during neuronal differentiation via CAP/ponsin and Rho GTPases.Eur J Cell Biol. 2008 Dec;87(12):921-31. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2008.07.001. Epub 2008 Aug 21. Eur J Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18722032
-
Microdomain-forming proteins and the role of the reggies/flotillins during axon regeneration in zebrafish.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Mar;1812(3):415-22. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2010.12.004. Epub 2010 Dec 13. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 21147218 Review.
-
Upregulation of reggie-1/flotillin-2 promotes axon regeneration in the rat optic nerve in vivo and neurite growth in vitro.Neurobiol Dis. 2013 Mar;51:168-76. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2012.11.007. Epub 2012 Nov 19. Neurobiol Dis. 2013. PMID: 23174179
-
Substrate properties of zebrafish Rtn4b/Nogo and axon regeneration in the zebrafish optic nerve.J Comp Neurol. 2017 Oct 1;525(14):2991-3009. doi: 10.1002/cne.24253. Epub 2017 Jun 23. J Comp Neurol. 2017. PMID: 28560734
-
How reggies regulate regeneration and axon growth.Cell Tissue Res. 2012 Jul;349(1):71-7. doi: 10.1007/s00441-012-1343-6. Epub 2012 Feb 15. Cell Tissue Res. 2012. PMID: 22350847 Review.
Cited by
-
Expression of flotillin-2 in human non-small cell lung cancer and its correlation with tumor progression and patient survival.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Jan 1;8(1):601-7. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 25755751 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear estrogen receptor activation by insulin-like growth factor-1 in Neuro-2A neuroblastoma cells requires endogenous estrogen synthesis and is mediated by mutually repressive MAPK and PI3K cascades.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2019 Jun 15;490:68-79. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2019.04.007. Epub 2019 Apr 13. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2019. PMID: 30986444 Free PMC article.
-
Flotillins: At the Intersection of Protein S-Palmitoylation and Lipid-Mediated Signaling.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 26;21(7):2283. doi: 10.3390/ijms21072283. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32225034 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomarkers and pathways in autism spectrum disorder: An individual meta-analysis based on proteomic and metabolomic data.Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2024 Oct 3. doi: 10.1007/s00406-024-01922-9. Online ahead of print. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39361099
-
Wnt secretion and gradient formation.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Mar 1;14(3):5130-45. doi: 10.3390/ijms14035130. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23455472 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abramoff MD, Magelhaes PJ, Ram SJ. Image processing with ImageJ. Biophotonics Int. 2004;11:36–42.
-
- Aoki K, Nakamura T, Matsuda M. Spatio-temporal regulation of Rac1 and Cdc42 activity during nerve growth factor-induced neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:713–719. - PubMed
-
- Banzai Y, Miki H, Yamaguchi H, Takenawa T. Essential role of neural Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein in neurite extension in PC12 cells and rat hippocampal primary culture cells. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:11987–11992. - PubMed
-
- Baumann CA, Ribon V, Kanzaki M, Thurmond DC, Mora S, Shigematsu S, Bickel PE, Pessin JE, Saltiel AR. CAP defines a second signalling pathway required for insulin-stimulated glucose transport. Nature. 2000;407:202–207. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
