The posterior vermis of the cerebellum selectively inhibits 10-Hz sympathetic nerve discharge in anesthetized cats
- PMID: 19458278
- PMCID: PMC2711703
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpregu.90989.2008
The posterior vermis of the cerebellum selectively inhibits 10-Hz sympathetic nerve discharge in anesthetized cats
Abstract
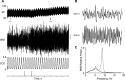
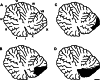
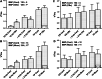
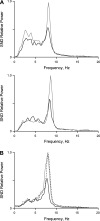
We studied the changes in inferior cardiac sympathetic nerve discharge (SND) and mean arterial pressure (MAP) produced by aspiration or chemical inactivation (muscimol microinjection) of lobule IX (uvula) of the posterior vermis of the cerebellum in baroreceptor-denervated and baroreceptor-innervated cats anesthetized with urethane. Autospectral analysis was used to decompose SND into its frequency components. Special attention was paid to the question of whether the experimental procedures affected the rhythmic (10-Hz and cardiac-related) components of SND. Aspiration or chemical inactivation of lobule IX produced an approximately three-fold increase in the 10-Hz rhythmic component of SND (P < or = 0.05) in baroreceptor-denervated cats. Total power (0- to 20-Hz band) was unchanged. Despite the absence of a change in total power in SND, there was a statistically significant increase in MAP. In baroreceptor-innervated cats, neither aspiration nor chemical inactivation of the uvula caused a significant change in cardiac-related or total power in SND or MAP. These results are the first to demonstrate a role of cerebellar cortical neurons of the posterior vermis in regulating the frequency composition of naturally occurring SND. Specifically, these neurons selectively inhibit the 10-Hz rhythm-generating network in baroreceptor-denervated, urethane-anesthetized cats. The functional implications of these findings are discussed.
Figures


References
-
- Barman SM, Gebber GL. Tonic sympathoinhibition in the baroreceptor-denervated cat. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 157: 646–653, 1978. - PubMed
-
- Barman SM, Gebber GL. 'Rapid' rhythmic discharges of sympathetic nerves: Sources, mechanisms of generation, and physiological relevance. J Biol Rhythms 15: 365–379, 2000. - PubMed
-
- Barman SM, Gebber GL, Kitchens H. Rostral dorsolateral pontine neurons with sympathetic nerve-related activity. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 276: H401–H412, 1999. - PubMed
-
- Barman SM, Gebber GL, Zhong S. The 10-Hz rhythm in sympathetic nerve discharge. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 262: R1006–R1014, 1992. - PubMed
-
- Barman SM, Kitchens HL, Leckow AB, Gebber GL. Pontine neurons are elements of the network responsible for the 10-Hz rhythm in sympathetic nerve discharge. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 273: H1909–H1919, 1997. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

