Cerebral microvascular endothelial cell Na/H exchange: evidence for the presence of NHE1 and NHE2 isoforms and regulation by arginine vasopressin
- PMID: 19458287
- PMCID: PMC2724093
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00093.2009
Cerebral microvascular endothelial cell Na/H exchange: evidence for the presence of NHE1 and NHE2 isoforms and regulation by arginine vasopressin
Abstract
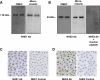
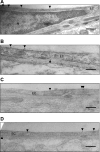
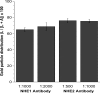
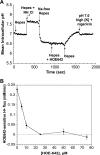
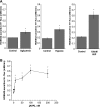
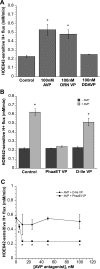
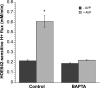
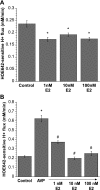
Blood-brain barrier (BBB) Na transporters are essential for brain water and electrolyte homeostasis. However, they also contribute to edema formation during the early hours of ischemic stroke by increased transport of Na from blood into brain across an intact BBB. We previously showed that a luminal BBB Na-K-Cl cotransporter is stimulated by hypoxia, aglycemia, and AVP and that inhibition of the cotransporter by intravenous bumetanide significantly reduces edema and infarct in the rat middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) model of stroke. More recently, we found evidence that intravenous cariporide (HOE-642), a highly potent Na/H exchange inhibitor, also reduces brain edema after MCAO. The present study was conducted to investigate which Na/H exchange protein isoforms are present in BBB endothelial cells and to evaluate the effects of ischemic factors on BBB Na/H exchange activity. Western blot analysis of bovine cerebral microvascular endothelial cells (CMEC) and immunoelectron microscopy of perfusion-fixed rat brain revealed that Na/H exchanger isoforms 1 and 2 (NHE1 and NHE2) are present in BBB endothelial cells. Using microspectrofluorometry and the pH-sensitive dye BCECF, we found that hypoxia (2% O(2), 30 min), aglycemia (30 min), and AVP (1-200 nM, 5 min) significantly increased CMEC Na/H exchange activity, assessed as Na-dependent, HOE-642-sensitive H(+) flux. We found that AVP stimulation of CMEC Na/H exchange activity is dependent on intracellular Ca concentration and is blocked by V(1), but not V(2), vasopressin receptor antagonists. Our findings support the hypothesis that a BBB Na/H exchanger, possibly NHE1 and/or NHE2, is stimulated during ischemia to participate in cerebral edema formation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ischemic factor-induced increases in cerebral microvascular endothelial cell Na/H exchange activity and abundance: evidence for involvement of ERK1/2 MAP kinase.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2014 May 15;306(10):C931-42. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00021.2013. Epub 2014 Mar 19. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24647544 Free PMC article.
-
Ischemia-induced stimulation of Na-K-Cl cotransport in cerebral microvascular endothelial cells involves AMP kinase.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2011 Aug;301(2):C316-26. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00517.2010. Epub 2011 May 11. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21562306 Free PMC article.
-
Arginine vasopressin stimulation of cerebral microvascular endothelial cell Na-K-Cl cotransporter activity is V1 receptor and [Ca] dependent.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2005 Aug;289(2):C283-92. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00001.2005. Epub 2005 Mar 30. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15800057
-
Blood-brain barrier Na transporters in ischemic stroke.Adv Pharmacol. 2014;71:113-46. doi: 10.1016/bs.apha.2014.06.011. Epub 2014 Aug 23. Adv Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25307215 Review.
-
Physiology and pathophysiology of Na+/H+ exchange and Na+ -K+ -2Cl- cotransport in the heart, brain, and blood.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2006 Jul;291(1):R1-25. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00782.2005. Epub 2006 Feb 16. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16484438 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of the global gene expression of choroid plexus and meninges and associated vasculature under control conditions and after pronounced hyperthermia or amphetamine toxicity.BMC Genomics. 2013 Mar 5;14:147. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-147. BMC Genomics. 2013. PMID: 23497014 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of estradiol on ischemic factor-induced astrocyte swelling and AQP4 protein abundance.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2011 Jul;301(1):C204-12. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00399.2010. Epub 2011 Apr 6. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21471464 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebral Edema Formation After Stroke: Emphasis on Blood-Brain Barrier and the Lymphatic Drainage System of the Brain.Front Cell Neurosci. 2021 Aug 16;15:716825. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2021.716825. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34483842 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High glucose-induced effects on Na+-K+-2Cl- cotransport and Na+/H+ exchange of blood-brain barrier endothelial cells: involvement of SGK1, PKCβII, and SPAK/OSR1.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2021 Apr 1;320(4):C619-C634. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00177.2019. Epub 2021 Jan 6. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33406028 Free PMC article.
-
Blood-brain barrier integrity and glial support: mechanisms that can be targeted for novel therapeutic approaches in stroke.Curr Pharm Des. 2012;18(25):3624-44. doi: 10.2174/138161212802002625. Curr Pharm Des. 2012. PMID: 22574987 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aharonovitz O, Granot Y. Stimulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase and Na+/H+ exchanger in human platelets. Differential effect of phorbol ester and vasopressin. J Biol Chem 271: 16494–16499, 1996. - PubMed
-
- Baird NR, Orlowski J, Szabó EZ, Zaun HC, Schultheis PJ, Menon AG, and Shull GE. Molecular cloning, genomic organization, and functional expression of Na+/H+ exchanger isoform 5 (NHE5) from human brain. J Biol Chem 274: 4377–4382, 1999. - PubMed
-
- Bauer B, Hartz AM, Fricker G, Miller DS. Pregnane X receptor up-regulation of P-glycoprotein expression and transport function at the blood-brain barrier. Mol Pharmacol 66: 413–419, 2004. - PubMed
-
- Betz AL Alterations in cerebral endothelial cell function in ischemia. Adv Neurol 71: 301–313, 1996. - PubMed
-
- Betz AL Sodium transport from blood to brain: inhibition by furosemide and amiloride. J Neurochem 41: 1158–1164, 1983. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

