Comprehensive analysis of the impact of SNPs and CNVs on human microRNAs and their regulatory genes
- PMID: 19458495
- PMCID: PMC2783774
- DOI: 10.4161/rna.6.4.8830
Comprehensive analysis of the impact of SNPs and CNVs on human microRNAs and their regulatory genes
Abstract
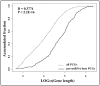
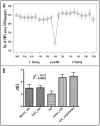
Human microRNAs (miRNAs) are potent regulators of gene expression and thus involved in a broad range of biological processes. The objective of this study was to update the properties of human miRNAs and to search for SNPs and CNVs with potential effects on them. Based on the miRBase 13.0 database, we identified 380 (53.9%) precursor miRNAs (pre-miRNAs) embedded in gene loci that are enriched in biological processes such as "neuronal activities", "cell cycle" and "protein phosphorylation" (Bonferroni p < 0.05). Gene lengths of the pre-miRNA host genes are significantly larger than other genes in the genome (p < 2.2E-16). Using data mining public resources, we performed a genome-scale search for the regulatory polymorphisms in the loci of pre-miRNAs and their related genes. Altogether, we found 187 SNPs in the pre-miRNAs, 497 consensus SNPs in the seed-matching untranslated regions of target genes, 385 CNVs harboring pre-miRNA precursors and 9 CNVs covering important miRNA processing genes. We also noticed that minimum free energy changed by pre-miRNA-residing SNPs could be ranked by the order from low to high as the SNPs in the loop domain, the SNPs in the adjacent stem and basal stem domains, and the SNPs in mature miRNA and its complementary sequence domains (p = 0.0065). With a full list of miRNA-related polymorphisms, this study will facilitate future association studies between the genetic polymorphisms in miRNA targets or pre-miRNAs and the disease susceptibility or therapeutic outcome.
Figures

Similar articles
-
miRNASNP-v3: a comprehensive database for SNPs and disease-related variations in miRNAs and miRNA targets.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Jan 8;49(D1):D1276-D1281. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa783. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 32990748 Free PMC article.
-
Single nucleotide polymorphism associated with mature miR-125a alters the processing of pri-miRNA.Hum Mol Genet. 2007 May 1;16(9):1124-31. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddm062. Epub 2007 Mar 30. Hum Mol Genet. 2007. PMID: 17400653
-
Copy number variation of microRNA genes in the human genome.BMC Genomics. 2011 Apr 12;12:183. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-183. BMC Genomics. 2011. PMID: 21486463 Free PMC article.
-
microRNA single polynucleotide polymorphism influences on microRNA biogenesis and mRNA target specificity.Gene. 2018 Jan 15;640:66-72. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2017.10.021. Epub 2017 Oct 13. Gene. 2018. PMID: 29032146 Review.
-
miRNAs, single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and age-related macular degeneration (AMD).Clin Chem Lab Med. 2017 May 1;55(5):763-775. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2016-0898. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2017. PMID: 28343170 Review.
Cited by
-
Resolving the variable genome and epigenome in human disease.J Intern Med. 2012 Apr;271(4):379-91. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2796.2011.02508.x. J Intern Med. 2012. PMID: 22443201 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The associations and roles of microRNA single-nucleotide polymorphisms in cervical cancer.Int J Med Sci. 2021 Apr 7;18(11):2347-2354. doi: 10.7150/ijms.57990. eCollection 2021. Int J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 33967611 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MiRNA genes constitute new targets for microsatellite instability in colorectal cancer.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e31862. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031862. Epub 2012 Feb 14. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22348132 Free PMC article.
-
Nei Endonuclease VIII-like 2 Gene rs8191670 Polymorphism affects the Sensitivity of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer to Cisplatin by binding with MiR-548a.J Cancer. 2020 Jun 6;11(16):4801-4809. doi: 10.7150/jca.47495. eCollection 2020. J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32626527 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the miR-34a locus in 62 patients with familial cutaneous melanoma negative for CDKN2A/CDK4 screening.Fam Cancer. 2012 Jun;11(2):201-8. doi: 10.1007/s10689-011-9502-6. Fam Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22198089
References
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–97. - PubMed
-
- Roush S, Slack FJ. The let-7 family of microRNAs. Trends Cell Biol. 2008;18:505–16. - PubMed
-
- Liu J. Control of protein synthesis and mRNA degradation by microRNAs. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2008;20:214–21. - PubMed
-
- Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP. Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 2005;120:15–20. - PubMed
-
- Croce CM, Calin GA. miRNAs, cancer and stem cell division. Cell. 2005;122:6–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
