Aptamers and aptamer targeted delivery
- PMID: 19458497
- PMCID: PMC4821413
- DOI: 10.4161/rna.6.3.8808
Aptamers and aptamer targeted delivery
Abstract
When aptamers first emerged almost two decades ago, most were RNA species that bound and tagged or inhibited simple target ligands. Very soon after, the 'selectionologists' developing aptamer technology quickly realized more potential for the aptamer. In recent years, advances in aptamer techniques have enabled the use of aptamers as small molecule inhibitors, diagnostic tools and even therapeutics. Aptamers are now being employed in novel applications. We review, herein, some of the recent and exciting applications of aptamers in cell-specific recognition and delivery.
Figures
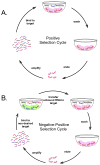
Similar articles
-
Aptamers as therapeutics.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2010 Jul;9(7):537-50. doi: 10.1038/nrd3141. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2010. PMID: 20592747 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic applications of synthetic nucleic acid aptamers.Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2017 Dec;48:180-186. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2017.05.004. Epub 2017 Jun 2. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 28582756 Review.
-
Using aptamers for targeted delivery of RNA therapies.Mol Ther. 2025 Apr 2;33(4):1344-1367. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2025.02.047. Epub 2025 Mar 5. Mol Ther. 2025. PMID: 40045577 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Smart functional nucleic acid chimeras: enabling tissue specific RNA targeting therapy.RNA Biol. 2015;12(4):412-25. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2015.1017234. RNA Biol. 2015. PMID: 25849197 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expected and unexpected features of protein-binding RNA aptamers.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2016 Nov;7(6):744-757. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1360. Epub 2016 May 12. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2016. PMID: 27173731 Review.
Cited by
-
Optimizing siRNA delivery to the genital mucosa.Discov Med. 2011 Feb;11(57):124-32. Discov Med. 2011. PMID: 21356167 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in aptamer-based biosensing technology for isolation and detection of extracellular vesicles.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Jul 23;13:1555687. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1555687. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40772226 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Promising new assays and technologies for the diagnosis and management of infectious diseases.Clin Infect Dis. 2013 Apr;56(7):996-1002. doi: 10.1093/cid/cis1014. Epub 2012 Dec 7. Clin Infect Dis. 2013. PMID: 23223587 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HAPIscreen, a method for high-throughput aptamer identification.J Nanobiotechnology. 2011 Jun 3;9:25. doi: 10.1186/1477-3155-9-25. J Nanobiotechnology. 2011. PMID: 21639912 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Detection of Nasty Bugs, Prevention Is Better than Cure.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 25;22(1):149. doi: 10.3390/ijms22010149. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33375709 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor therapy for subfoveal choroidal neovascularization secondary to age-related macular degeneration: phase II study results. Ophthalmology. 2003;110:979–86. - PubMed
-
- Chan MY, Cohen MG, Dyke CK, Myles SK, Aberle LG, Lin M, et al. Phase 1b randomized study of antidote-controlled modulation of factor IXa activity in patients with stable coronary artery disease. Circulation. 2008;117:2865–74. - PubMed
-
- Alexander JH, Hafley G, Harrington RA, Peterson ED, Ferguson TB, Jr, Lorenz TJ, et al. Efficacy and safety of edifoligide, an E2F transcription factor decoy, for prevention of vein graft failure following coronary artery bypass graft surgery: PREVENT IV: a randomized controlled trial. Jama. 2005;294:2446–54. - PubMed
-
- Gilbert JC, DeFeo-Fraulini T, Hutabarat RM, Horvath CJ, Merlino PG, Marsh HN, et al. First-in-human evaluation of anti von Willebrand factor therapeutic aptamer ARC1779 in healthy volunteers. Circulation. 2007;116:2678–86. - PubMed
-
- Apte RS, Modi M, Masonson H, Patel M, Whitfield L, Adamis AP. Pegaptanib 1-year systemic safety results from a safety-pharmacokinetic trial in patients with neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Ophthalmology. 2007;114:1702–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
